Association between Hpa Axis Functioning and Mental Health in Maltreated Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 37628343
- PMCID: PMC10453675
- DOI: 10.3390/children10081344
Association between Hpa Axis Functioning and Mental Health in Maltreated Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have demonstrated that children who experience maltreatment show a more elevated risk of psychopathological disorders than children from the general population. The HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis is not mature at birth and undergoes strong social regulation during the first years of life. Consequently, early exposure to stress could modify the usual adaptative response to stress. In stressful situations, perturbations in both cortisol response and cortisol circadian rhythm have been observed. Nevertheless, studies that have evaluated the links between child abuse, dysregulation of the HPA axis, and mental disorders have shown diverse results. Because of the variety of methods employed in the different studies, no formal comparisons have been made. In this systematic review, we have brought together these results.
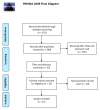
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of studies analyzing the correlation between child abuse, mental disorders, and HPA axis activity in patients aged between 6 and 16 years. PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Google Scholar were searched using relevant keywords and inclusion/exclusion criteria (from 2000 to 2020).
Results: Fifteen studies from the 351 identified were included. Most patients were children in the child welfare system. Children who had experienced child abuse presented with more severe mental disorders (particularly in the dimensional measure) than children who had not been abused. HPA axis activity was assessed by measuring basal cortisol for some studies and cortisol reactivity for other studies. For children experiencing child abuse, there was a possible association between abuse and a decrease in the reactivity of the HPA axis. In addition, early life stress could be associated with lower matinal cortisol. However, the association between mental disorders and cortisol secretion in maltreated children did not seem obvious.
Conclusions: This systematic review demonstrates that mental disorders are more frequent and severe in cases where child abuse has occurred. Moreover, children who experienced child abuse seem to present changes in the reactivity of the HPA axis. Nevertheless, the potential correlation between these changes in the reactivity of the HPA axis and mental disorders in this population needs to be evaluated in further studies.
Keywords: behavior disorders; childhood; cortisol; hypothalamo hypophyseal system; physiological stress reactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Soins-Maternels-et-Sante-Mentale-Bowby-OMS-1951.pdf. [(accessed on 23 February 2020)]. Available online: http://psyfontevraud.free.fr/AARP/psyangevine/Documents-historiques/Soin....
-
- Benarous X., Consoli A., Raffin M., Cohen D. Abus, maltraitance et négligence: (1) épidémiologie et retentissements psychiques, somatiques et sociaux. Neuropsychiatr. Enfance Adolescence. 2014;62:299–312. doi: 10.1016/j.neurenf.2014.04.005. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources