Universal Design for Learning for Children with ADHD
- PMID: 37628349
- PMCID: PMC10453933
- DOI: 10.3390/children10081350
Universal Design for Learning for Children with ADHD
Abstract
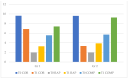
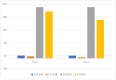
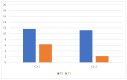
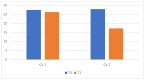
Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a psychiatric condition that shows developmentally inappropriate levels of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity. Symptoms begin at a young age and usually include a lack of attention, poor concentration, disorganization, difficulty completing tasks, forgetfulness, and losing things. It is important to diagnose and treat the disorder at a young age so that the symptoms do not persist into adulthood and cause other comorbid conditions. Learning difficulties, motor impairment, anxiety, or depressive disorders may occur with this condition. To improve the academic careers of children with ADHD, we focused on a specific innovative educational approach (Universal Design for Learning) that could improve basic learning skills (reading, writing, and arithmetic skills) to prevent or manage any learning difficulty that could occur with ADHD. The Universal Design for Learning is an individualized approach that combines current neuroscientific knowledge, creating personalized teaching based on the strengths and weaknesses of the student. The goal of this study is to analyze the impact that this approach has on basic learning abilities. We found that both interventions led to improvements in test performance, indicating that interventions were necessary to enhance reading, writing, and arithmetic skills. Furthermore, the group that received an educational intervention based on Universal Design for Learning demonstrated a more significant improvement in these areas. Additionally, we propose that the set of techniques implemented by teachers in the classroom helped children to read, write, and perform math tasks correctly and more fluently.
Keywords: ADHD; Universal Design for Learning: learning; hyperactivity; impulsivity; teaching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Magnus W., Nazir S., Anilkumar A.C., Shaban K. StatPearls. StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. - PubMed
-
- Barkley R.A. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment. 3rd ed. The Guilford Press; New York, NY, USA: 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources