Treatment of Upper Crossed Syndrome: A Narrative Systematic Review
- PMID: 37628525
- PMCID: PMC10454745
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11162328
Treatment of Upper Crossed Syndrome: A Narrative Systematic Review
Abstract
Background and objectives: Upper crossed syndrome (UCS) is a common musculoskeletal condition that is characterized by tightness and weakness of the muscles of the neck, shoulders, and upper back. The aim of this current study is to summarize and provide an overview of the treatment in patients with UCS.
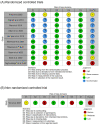
Materials and methods: A MEDLINE (PubMed), Cochrane library, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science database search was conducted for English-language articles about upper crossed syndrome that were published until 19 January 2023. To identify potentially relevant articles, the following key search phrases were combined: "upper crossed syndrome", "upper cross syndrome", "diagnosis", and "treatment". A total of 233 articles were identified. After reading the titles and abstracts and assessing their eligibility based on the full-text articles, 11 articles were finally included in this review. The risk of bias (RoB) was assessed using RoB-2 and ROBINS-I for the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and the non-randomized clinical trial (non-RCT), respectively.
Results: Among eleven studies that investigated the effect of treatment programs for UCS, five studies compared the therapeutic effect of exercise programs with controls, whereas six compared different rehabilitative treatment strategies, such as the muscle energy technique, soft-tissue mobilization, and stretching exercises. In addition, regarding the study design, ten studies were RCTs and only one study was a prospective observational study.
Conclusions: Treatment programs including various types of exercises and techniques to correct an abnormal posture and restore neuromuscular imbalances are effective for decreasing pain and improving neck disabilities and postural deviations in patients with UCS.
Keywords: musculoskeletal diseases; musculoskeletal manipulations; musculoskeletal pain; pain; pain management; postural balance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Page P., Frank C.C., Lardner R. Assessment and Treatment of Muscle Imbalance: The Janda Approach. Human Kinetics; Champaign, IL, USA: 2009.
-
- Morris C.E., Bonnefin D., Darville C. The Torsional Upper Crossed Syndrome: A multi-planar update to Janda’s model, with a case series introduction of the mid-pectoral fascial lesion as an associated etiological factor. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2015;19:681–689. - PubMed
-
- Kibler W.B., Sciascia A. Current concepts: Scapular dyskinesis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010;44:300–305. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical