Exploring the Binding Affinity of the ARR2 GARP DNA Binding Domain via Comparative Methods
- PMID: 37628689
- PMCID: PMC10454580
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14081638
Exploring the Binding Affinity of the ARR2 GARP DNA Binding Domain via Comparative Methods
Abstract
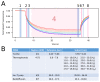
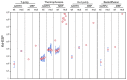
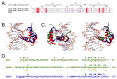
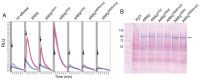
Plants have evolved signaling mechanisms such as the multi-step phosphorelay (MSP) to respond to different internal and external stimuli. MSP responses often result in gene transcription regulation that is modulated through transcription factors such as B-type Arabidopsis response regulator (ARR) proteins. Among these proteins, ARR2 is a key component that is expressed ubiquitously and is involved in many aspects of plant development. Although it has been noted that B-type ARRs bind to their cognate genes through a DNA-binding domain termed the GARP domain, little is known about the structure and function of this type of DNA-binding domain; thus, how ARRs bind to DNA at a structural level is still poorly understood. In order to understand how the MSP functions in planta, it is crucial to unravel both the kinetics as well as the structural identity of the components involved in such interactions. For this reason, this work focusses on resolving how the GARP domain of ARR2 (GARP2) binds to the promoter region of ARR5, one of its native target genes in cytokinin signaling. We have established that GARP2 specifically binds to the ARR5 promoter with three different bi-molecular interaction systems-qDPI-ELISA, FCS, and MST-and we also determined the KD of this interaction. In addition, structural modeling of the GARP2 domain confirms that GARP2 entails a HTH motif, and that protein-DNA interaction most likely occurs via the α3-helix and the N-terminal arm of this domain since mutations in this region hinder ARR2's ability to activate transcription.
Keywords: ARR2; DPI-ELISA; FCS; GARP; MST; reporter gene; structural modeling; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cytokinin-facilitated proteolysis of ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATOR 2 attenuates signaling output in two-component circuitry.Plant J. 2012 Mar;69(6):934-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04843.x. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22050482
-
Attenuation of cytokinin signaling via proteolysis of a type-B response regulator.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Jul;7(7):756-9. doi: 10.4161/psb.20469. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22751310 Free PMC article.
-
In planta analysis of a cis-regulatory cytokinin response motif in Arabidopsis and identification of a novel enhancer sequence.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Jul;54(7):1079-92. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct060. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23620480
-
The world according to GARP transcription factors.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017 Oct;39:159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28802165 Review.
-
The Interaction Network and Signaling Specificity of Two-Component System in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 11;21(14):4898. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144898. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32664520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

