The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Epigenetic Regulation of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37628735
- PMCID: PMC10454626
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241612555
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Epigenetic Regulation of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
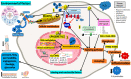
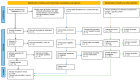
This review explores the emerging role of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in modulating epigenetic mechanisms involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Accumulating evidence has begun to elucidate the multifaceted ways in which H2S influences the epigenetic landscape and, subsequently, the progression of various neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease. H2S can modulate key components of the epigenetic machinery, such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs, impacting gene expression and cellular functions relevant to neuronal survival, inflammation, and synaptic plasticity. We synthesize recent research that positions H2S as an essential player within this intricate network, with the potential to open new therapeutic avenues for these currently incurable conditions. Despite significant progress, there remains a considerable gap in our understanding of the precise molecular mechanisms and the potential therapeutic implications of modulating H2S levels or its downstream targets. We conclude by identifying future directions for research aimed at exploiting the therapeutic potential of H2S in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; DNA methylation; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; epigenetic regulation; histone modifications; hydrogen sulfide; neurodegenerative diseases; non-coding RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intersection of H2S and Nrf2 signaling: Therapeutic opportunities for neurodegenerative diseases.Neurotherapeutics. 2025 Jun 21:e00627. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2025.e00627. Online ahead of print. Neurotherapeutics. 2025. PMID: 40544135 Review.
-
The Role of DNA Methylation and Histone Modifications in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 14;11(12):e0167201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167201. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27973581 Free PMC article.
-
[Epigenetics' implication in autism spectrum disorders: A review].Encephale. 2017 Aug;43(4):374-381. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 27692350 French.
-
Epigenetic reprogramming as a therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases: A complex and novel approach.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 5;1002:177853. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177853. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40541595 Review.
-
Advancements in CRISPR-Based Therapies for Genetic Modulation in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Curr Gene Ther. 2025;25(1):34-45. doi: 10.2174/0115665232292246240426125504. Curr Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 38738727 Review.
Cited by
-
The Janus Face of Oxidative Stress and Hydrogen Sulfide: Insights into Neurodegenerative Disease Pathogenesis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 19;14(3):360. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030360. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation.Open Med (Wars). 2025 May 17;20(1):20251201. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1201. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40391079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Localization and Structural-Functional Organization of p53 Following Traumatic Brain Injury: Development of a YOLO Model for Detection and Quantification of Apoptotic Nuclei.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 24;26(11):5066. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115066. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507878 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Localization and Expression of p53 and Cell Death in the Nervous Tissue in Traumatic Brain Injury and Axotomy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 28;24(21):15708. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115708. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958692 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hydrogen sulfide regulation of ferroptosis in different diseases.Apoptosis. 2024 Oct;29(9-10):1377-1392. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01992-z. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38980600 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

