Targeting Heat Shock Protein 27 and Fatty Acid Oxidation Augments Cisplatin Treatment in Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 37628819
- PMCID: PMC10454186
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241612638
Targeting Heat Shock Protein 27 and Fatty Acid Oxidation Augments Cisplatin Treatment in Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
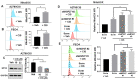
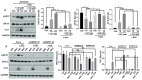
Most ovarian cancer patients develop recurrent cancers which are often resistant to commonly employed chemotherapy agents, such as cisplatin. We have previously shown that the inhibition of heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) or fatty acid oxidation (FAO) sensitizes cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines to cisplatin and dual inhibition of both HSP27 and FAO induces substantial cell death in vitro. However, it is unclear how HSP27 and FAO promote cisplatin resistance, and if dual inhibition of both HSP27 and FAO would augment cisplatin treatment in vivo. Here we showed that HSP27 knockdown in two cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines (A2780CIS and PEO4) resulted in more ROS production upon cisplatin treatment. HSP27-knockdown cancer cells exhibited decreased levels of reduced glutathione (GSH) and glucose6phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), a crucial pentose phosphate pathway enzyme. ROS depletion with the compound N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) attenuated cisplatin-induced upregulation of HSP27, FAO, and markers of apoptosis and ferroptosis in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Finally, inhibition of HSP27 and FAO with ivermectin and perhexiline enhanced the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin in A2780CIS xenograft tumors in vivo. Our results suggest that two different cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines upregulate HSP27 and FAO to deplete cisplatin-induced ROS to attenuate cisplatin's cytotoxic effect.
Keywords: FAO; HSP27; ROS; cisplatin resistance; ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role and mechanism of fatty acid oxidation in cancer drug resistance.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jun 13;11(1):277. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02554-1. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40514365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat Shock Protein 27, a Novel Downstream Target of Collagen Type XI alpha 1, Synergizes with Fatty Acid Oxidation to Confer Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;13(19):4855. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194855. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638339 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of collagen XI alpha 1-induced fatty acid oxidation triggers apoptotic cell death in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Apr 20;11(4):258. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2442-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32312965 Free PMC article.
-
HSP27 Knockdown Increases Cytoplasmic p21 and Cisplatin Sensitivity in Ovarian Carcinoma Cells.Oncol Res. 2016;23(3):119-28. doi: 10.3727/096504015X14496932933656. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 26931434 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hsp27 in Chemotherapy Resistance.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 14;10(4):897. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040897. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HSP27/IL-6 axis promotes OSCC chemoresistance, invasion and migration by orchestrating macrophages via a positive feedback loop.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 28;41(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09983-1. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39873845 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of small extracellular vesicles in metabolic reprogramming and drug resistance in cancers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Sep 27;7:38. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.81. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39403606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and mechanism of fatty acid oxidation in cancer drug resistance.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jun 13;11(1):277. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02554-1. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40514365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ferroptosis: a promising avenue for ovarian cancer treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1578723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1578723. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2022. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2022.
-
- Nallanthighal S., Rada M., Heiserman J.P., Cha J., Sage J., Zhou B., Yang W., Hu Y., Korgaonkar C., Hanos C.T., et al. Inhibition of collagen XI alpha 1-induced fatty acid oxidation triggers apoptotic cell death in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:258. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2442-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heiserman J.P., Nallanthighal S., Gifford C.C., Graham K., Samarakoon R., Gao C., Sage J.J., Zhang W., Higgins P.J., Cheon D.J. Heat Shock Protein 27, a Novel Downstream Target of Collagen Type XI alpha 1, Synergizes with Fatty Acid Oxidation to Confer Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2021;13:4855. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

