Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP), Its Isoforms and the Interplay with the Epithelium in Allergy and Asthma
- PMID: 37628907
- PMCID: PMC10454039
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241612725
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP), Its Isoforms and the Interplay with the Epithelium in Allergy and Asthma
Abstract
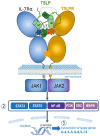
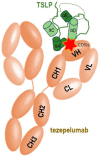
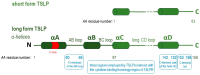
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a pleiotropic cytokine that has emerged as a critical player in the development and progression of allergy and asthma. It is primarily produced by epithelial cells and functions as a potent immune system activator. TSLP acts through interaction with its receptor complex, composed of the TSLP receptor (TSLPR) and interleukin-7 receptor alpha chain (IL-7Rα), activating downstream complex signalling pathways. The TSLP major isoform, known as long-form TSLP (lfTSLP), is upregulated in the airway epithelium of patients with allergic diseases. More research is warranted to explore the precise mechanisms by which short-form TSLP (sfTSLP) regulates immune responses. Understanding the dynamic interplay between TSLP and the dysfunctional epithelium provides insights into the mechanisms underlying allergy and asthma pathogenesis. Targeting TSLP represents an important therapeutic strategy, as it may upstream disrupt the inflammatory cascade and alleviate symptoms associated with allergic inflammation.
Keywords: allergy; asthma; epithelium; thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Allakhverdi Z., Comeau M.R., Jessup H.K., Yoon B.-R.P., Brewer A., Chartier S., Paquette N., Ziegler S.F., Sarfati M., Delespesse G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007;204:253–258. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062211. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee H.-C., Headley M.B., Loo Y.-M., Berlin A., Gale M., Debley J.S., Lukacs N.W., Ziegler S.F. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is induced by respiratory syncytial virus–infected airway epithelial cells and promotes a type 2 response to infection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;130:1187–1196.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

