Discovery of α-Linolenic Acid 16(S)-Lipoxygenase: Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Vegetative Lipoxygenase 3
- PMID: 37629162
- PMCID: PMC10454662
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241612977
Discovery of α-Linolenic Acid 16(S)-Lipoxygenase: Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Vegetative Lipoxygenase 3
Abstract
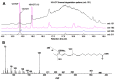
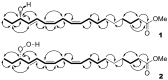
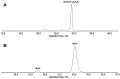
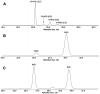
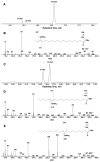
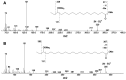
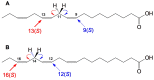
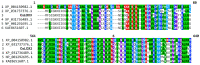
The GC-MS profiling of the endogenous oxylipins (Me/TMS) from cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) leaves, flowers, and fruit peels revealed a remarkable abundance of 16-hydroxy-9,12,14-octadecatrienoic acid (16-HOT). Incubations of homogenates from these organs with α-linolenic acid yielded 16(S)-hydroperoxide (16-HPOT) as a predominant product. Targeted proteomic analyses of these tissues revealed the presence of several highly homologous isoforms of the putative "9S-lipoxygenase type 6". One of these isoenzymes (CsLOX3, an 877 amino acid polypeptide) was prepared by heterologous expression in E. coli and exhibited 16(S)- and 13(S)-lipoxygenase activity toward α-linolenic and linoleic acids, respectively. Furthermore, α-linolenate was a preferred substrate. The molecular structures of 16(S)-HOT and 16(S)-HPOT (Me or Me/TMS) were unequivocally confirmed by the mass spectral data, 1H-NMR, 2D 1H-1H-COSY, TOCSY, HMBC, and HSQC spectra, as well as enantiomeric HPLC analyses. Thus, the vegetative CsLOX3, biosynthesizing 16(S)-HPOT, is the first 16(S)-LOX and ω3-LOX ever discovered. Eicosapentaenoic and hexadecatrienoic acids were also specifically transformed to the corresponding ω3(S)-hydroperoxides by CsLOX3.
Keywords: cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.); fatty acid hydroperoxides; lipoxygenase; molecular cloning; ω3 fatty acids; ω3(S) dioxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

