Research Progress of Macromolecules in the Prevention and Treatment of Sepsis
- PMID: 37629199
- PMCID: PMC10455590
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241613017
Research Progress of Macromolecules in the Prevention and Treatment of Sepsis
Abstract
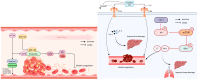
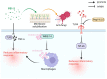
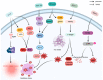
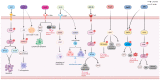
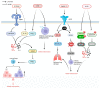
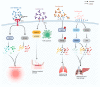
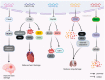
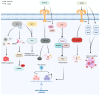
Sepsis is associated with high rates of mortality in the intensive care unit and accompanied by systemic inflammatory reactions, secondary infections, and multiple organ failure. Biological macromolecules are drugs produced using modern biotechnology to prevent or treat diseases. Indeed, antithrombin, antimicrobial peptides, interleukins, antibodies, nucleic acids, and lentinan have been used to prevent and treat sepsis. In vitro, biological macromolecules can significantly ameliorate the inflammatory response, apoptosis, and multiple organ failure caused by sepsis. Several biological macromolecules have entered clinical trials. This review summarizes the sources, efficacy, mechanism of action, and research progress of macromolecular drugs used in the prevention and treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: RNA; antibody; biomolecule; polypeptide; polysaccharide; protein; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antithrombin III in patients with severe sepsis. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind multicenter trial plus a meta-analysis on all randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials with antithrombin III in severe sepsis.Intensive Care Med. 1998 Jul;24(7):663-72. doi: 10.1007/s001340050642. Intensive Care Med. 1998. PMID: 9722035 Clinical Trial.
-
Sepsis and organ dysfunction/failure. An overview.Minerva Anestesiol. 1999 Jul-Aug;65(7-8):529-40. Minerva Anestesiol. 1999. PMID: 10479840 Review.
-
Caring for the critically ill patient. High-dose antithrombin III in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2001 Oct 17;286(15):1869-78. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.15.1869. JAMA. 2001. PMID: 11597289 Clinical Trial.
-
Human protein C zymogen concentrate in patients with severe sepsis and multiple organ failure after adult cardiac surgery.Intensive Care Med. 2009 Nov;35(11):1959-63. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1584-3. Epub 2009 Aug 1. Intensive Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19649614 Clinical Trial.
-
Pathogenesis of Multiple Organ Failure in Sepsis.Crit Rev Immunol. 2015;35(4):277-91. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2015015461. Crit Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26757392 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA DLEU1 contributes to the progression of septic myocardial dysfunction by targeting miR-381-3p.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024;49(3):227-237. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2024.144199. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39720275 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory mechanisms of decoy receptor 3 in cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis.mBio. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):e0052124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00521-24. Epub 2024 May 3. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38700314 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of turmeric kombucha ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis by attenuating inflammation and modulating gut microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1452190. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1452190. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Su J., Guo K., Huang M., Liu Y., Zhang J., Sun L., Li D., Pang K.L., Wang G., Chen L., et al. Fucoxanthin, a marine xanthophyll isolated from Conticribra weissflogii ND-8: Preventive anti-inflammatory effect in a mouse model of sepsis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019;10:906. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00906. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

