Acute Kidney Injury and Sepsis after Cardiac Surgery: The Roles of Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinase-2, Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-7, and Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin
- PMID: 37629236
- PMCID: PMC10455441
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12165193
Acute Kidney Injury and Sepsis after Cardiac Surgery: The Roles of Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinase-2, Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-7, and Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin
Abstract
Background: Identifying a panel of markers detecting kidney injury before the glomerular filtration rate reduction is a challenge to improving the diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury (AKI) in septic patients. This study evaluated the roles of tissue inhibitor metal proteinase-2, insulin growth factor binding protein-7 (TIMP2*IGFBP7), and mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in patients with AKI.
Patients and methods: This study was prospectively conducted in an intensive care unit (ICU) enrolling 230 patients who underwent cardiac surgery. Biomarkers were evaluated before and after 4 h of the cardiac surgery.
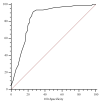
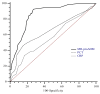
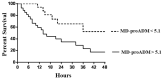
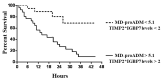
Results: Whereas urine and creatinine alterations appeared at 23.2 (12.7-36.5) hours after cardiac surgery, urinary TIMP2*IGBP7 levels were higher at 4 h in AKI patients (1.1 ± 0.4 mg/L vs. 0.08 ± 0.02 mg/L; p < 0.001). Its concentration > 2 mg/L increases AKI risk within the following 24 h, clearly identifying the population at high risk of renal replacement therapy (RRT). In patients with sepsis, MR-proADM levels were 2.3 nmol/L (0.7-7.8 nmol/L), with the highest values observed in septic shock patients (5.6 nmol/L (3.2-18 nmol/L)) and a better diagnostic profile than procalcitonin and C-reactive protein to identify septic patients. MR-proADM values > 5.1 nmol/L and urine TIMP2*IGBP7 levels > 2 mg/L showed a significantly faster progression to RRT, with a mean follow-up time of 1.1 days.
Conclusions: TIMP2*IGBP7 and MR-proADM precociously diagnose AKI in septic patients after cardiac surgery, giving prognostic information for RRT requirement.
Keywords: TIMP2*IGBP7; acute kidney injury; mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin Can Predict Organ Failure and Prognosis in Sepsis?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 13;24(24):17429. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417429. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139258 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 7 Deriving from Spleen and Lung Could Be Used for Early Recognition of Cardiac Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Cardiorenal Med. 2023;13(1):221-231. doi: 10.1159/000531489. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Cardiorenal Med. 2023. PMID: 37311433 Free PMC article.
-
MR-proAdrenomedullin as a predictor of renal replacement therapy in a cohort of critically ill patients with COVID-19.Biomarkers. 2021 Jul;26(5):417-424. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2021.1905067. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 33754916
-
New role of biomarkers: mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin, the biomarker of organ failure.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Sep;4(17):329. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.08.65. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27713887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic accuracy of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Minerva Anestesiol. 2021 Oct;87(10):1117-1127. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.21.15585-3. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021. PMID: 34134460
Cited by
-
In Vitro Simulated Hemoperfusion on Seraph®-100 as a Promising Strategy to Counteract Sepsis.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 5;12(3):575. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030575. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540188 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and clinical role of TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7 in cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 24;103(21):e38124. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038124. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38788006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of New Morphological Parameters Provided by the BC 6800 Plus Analyzer in the Early Diagnosis of Sepsis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;14(3):340. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030340. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337856 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoperfusion with Seraph-100 in septic patients removes pathogens and improves clinical outcomes.Sci Rep. 2025 May 21;15(1):17626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01280-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40399373 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis Biomarkers: Advancements and Clinical Applications-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 19;25(16):9010. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169010. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uchino S., Kellum J.A., Bellomo R., Doig G.S., Morimatsu H., Morgera S., Schetz M., Tan I., Bouman C., Macedo E., et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Lacquaniti A., Caccamo C., Salis P., Chirico V., Buemi A., Cernaro V., Noto A., Pettinato G., Santoro D., Bertani T., et al. Delayed graft function and chronic allograft nephropathy: Diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Biomarkers. 2016;21:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Murray P.T., Mehta R.L., Shaw A., Ronco C., Endre Z., Kellum J.A., Chawla L.S., Cruz D., Ince C., Okusa M.D. ADQI 10 workgroup Potential use of biomarkers in acute kidney injury: Report and summary of recommendations from the 10th Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative consensus conference. Kidney Int. 2020;180:513–521. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

