Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Pain Management in Hemodialysis: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37629432
- PMCID: PMC10455227
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12165390
Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Pain Management in Hemodialysis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
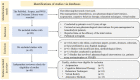
This narrative review aims to summarize non-pharmacological interventions for pain management in hemodialysis patients, assessing their potential benefits and limitations in enhancing patient well-being and quality of life. We reviewed the current literature on five primary non-pharmacological interventions: acupuncture, cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, virtual reality, and alternative methods such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, music therapy, and aromatherapy. We analyzed the evidence regarding their effectiveness, feasibility, and optimal implementation strategies. The existing evidence supports the potential benefits of these interventions in managing pain and improving the well-being of hemodialysis patients. However, further high-quality research is needed to confirm their effectiveness, establish implementation best practices, and assess their long-term impact on patient outcomes. Non-pharmacological interventions hold promise for pain management in hemodialysis patients. Additional research is required to optimize these interventions and validate their effectiveness, contributing to comprehensive pain management strategies for this vulnerable patient population.
Keywords: acupuncture; cognitive behavioral therapy; hemodialysis; pain management; relaxation techniques; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- dos Santos P.R., Mendonça C.R., Noll M., Borges C.C., Alves P.M., Dias N.T., Romeiro A.M.d.S., Barbosa M.A., Porto C.C. Pain in Hemodialysis Patients: Prevalence, Intensity, Location, and Functional Interference in Daily Activities. Healthcare. 2021;9:1375. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9101375. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources