Accelerated Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Toxicity Induced by Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 37629488
- PMCID: PMC10455250
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081631
Accelerated Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Toxicity Induced by Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer
Abstract
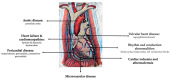
The number of patients diagnosed with breast cancer and cardiovascular disease is continuously rising. Treatment options for breast cancer have greatly evolved, but radiotherapy (RT) still has a key role in it. Despite many advances in RT techniques, cardiotoxicity is one of the most important side effects. The new cardio-oncology guidelines recommend a baseline evaluation, risk stratification and follow-up of these patients. Cardiotoxicity induced by RT can be represented by almost all forms of cardiovascular disease, with atherosclerosis being the most frequent. An interdisciplinary team should manage these patients, in order to have maximum therapeutic effect and minimum cardiovascular toxicity. This review will summarize the current incidence, risk factors, mechanisms and follow-up of RT-induced cardiovascular toxicity.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer; cardiovascular toxicity; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- [(accessed on 17 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/current-and-future-burden-of-breast...
-
- Lyon A.R., López-Fernández T., Couch L.S., Asteggiano R., Aznar M.C., Bergler-Klein J., Boriani G., Cardinale D., Cordoba R., Cosyns B., et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS) Eur. Heart J. 2022;43:4229–4361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac244. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacob S., Camilleri J., Derreumaux S., Walker V., Lairez O., Lapeyre M., Bruguière E., Pathak A., Bernier M.-O., Laurier D., et al. Is mean heart dose a relevant surrogate parameter of left ventricle and coronary arteries exposure during breast cancer radiotherapy: A dosimetric evaluation based on individually-determined radiation dose (BACCARAT study) Radiat. Oncol. 2019;14:29. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1234-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reed G.W., Masri A., Griffin B.P., Kapadia S.R., Ellis S.G., Desai M.Y. Long-term mortality in patients with radiation-associated coronary artery disease treated with percu-taneous coronary intervention. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016;9:e003483. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.115.003483. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuohinen S.S., Skyttä T., Poutanen T., Huhtala H., Virtanen V., Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P.-L., Raatikainen P. Radiotherapy-induced global and regional differences in early-stage left-sided versus right-sided breast cancer patients: Speckle tracking echocardiography study. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2017;33:463–472. doi: 10.1007/s10554-016-1021-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources