Antimicrobial Peptides in Infectious Diseases and Beyond-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37629508
- PMCID: PMC10455936
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081651
Antimicrobial Peptides in Infectious Diseases and Beyond-A Narrative Review
Abstract
Despite recent medical research and clinical practice developments, the development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) significantly limits therapeutics for infectious diseases. Thus, novel treatments for infectious diseases, especially in this era of increasing AMR, are urgently needed. There is ongoing research on non-classical therapies for infectious diseases utilizing alternative antimicrobial mechanisms to fight pathogens, such as bacteriophages or antimicrobial peptides (AMPs). AMPs are evolutionarily conserved molecules naturally produced by several organisms, such as plants, insects, marine organisms, and mammals, aiming to protect the host by fighting pathogenic microorganisms. There is ongoing research regarding developing AMPs for clinical use in infectious diseases. Moreover, AMPs have several other non-medical applications in the food industry, such as preservatives, animal husbandry, plant protection, and aquaculture. This review focuses on AMPs, their origins, biology, structure, mechanisms of action, non-medical applications, and clinical applications in infectious diseases.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial peptides; antimicrobial resistance; infectious diseases; microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
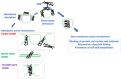
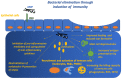
Similar articles
-
Revolutionizing agroindustry: Towards the industrial application of antimicrobial peptides against pathogens and pests.Biotechnol Adv. 2025 Sep;82:108605. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2025.108605. Epub 2025 May 12. Biotechnol Adv. 2025. PMID: 40368115 Review.
-
Production, Delivery, and Regulatory Aspects for Application of Plant-Based Anti-microbial Peptides: a Comprehensive Review.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jan 4. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10421-1. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39753941 Review.
-
Prospects of antimicrobial peptides as an alternative to chemical preservatives for food safety.Biotechnol Lett. 2023 Feb;45(2):137-162. doi: 10.1007/s10529-022-03328-w. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Biotechnol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36504266 Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): A promising class of antimicrobial compounds.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Mar;132(3):1573-1596. doi: 10.1111/jam.15314. Epub 2021 Oct 13. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34606679 Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: a new era for antibiotics.Can J Microbiol. 2015 Feb;61(2):93-103. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2014-0613. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Can J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25629960 Review.
Cited by
-
Expansion of the antibacterial spectrum of symmetrical amino acid-paired antifungal peptides through structural optimization.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Aug 8;25(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04160-8. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40775273 Free PMC article.
-
Serine protease inhibitor dipetalogastin-like from Galleria mellonella is involved in insect immunity.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 6;15(1):24094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08159-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40619466 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptides: a promising frontier to combat antibiotic resistant pathogens.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Mar 27;87(4):2118-2132. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003106. eCollection 2025 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40212220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predatory Bacteria in the Treatment of Infectious Diseases and Beyond.Infect Dis Rep. 2024 Jul 25;16(4):684-698. doi: 10.3390/idr16040052. Infect Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 39195003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the antimicrobial potential of crude peptide extracts from Allium sativum and Allium oschaninii against antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):666-675. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2395517. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 39205473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray C.J.L., Ikuta K.S., Sharara F., Swetschinski L., Aguilar G.R., Gray A., Han C., Bisignano C., Rao P., Wool E., et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet. 2022;399:629–655. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mestrovic T., Aguilar G.R., Swetschinski L.R., Ikuta K.S., Gray A.P., Weaver N.D., Han C., E Wool E., Hayoon A.G., Hay S.I., et al. The Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in the WHO European Region in 2019: A Cross-Country Systematic Analysis. Lancet Public Health. 2022;7:e897–e913. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(22)00225-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

