Box-Behnken Design for Assessing the Efficiency of Aflatoxin M1 Detoxification in Milk Using Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 37629525
- PMCID: PMC10456063
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081667
Box-Behnken Design for Assessing the Efficiency of Aflatoxin M1 Detoxification in Milk Using Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
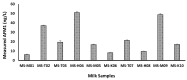
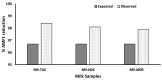
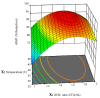
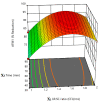
Milk contaminated with aflatoxin can lead to liver cancer. Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), a serious animal feed contaminant, is transformed into Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) and secreted in milk. In this study, a biological method using probiotic bacteria, Lactobacillus rhamnosus (L. rhamnosus) in combination with Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae), was used to assess their antiaflatoxigenic effect in animal milk. A Box-Behnken design was used to establish the optimal ratio of L. rhamnosus and S. cerevisiae, incubation time, and temperature for efficient AFM1 detoxification from milk. To achieve this, the primary, interaction, and quadratic effects of the chosen factors were investigated. To investigate the quadratic response surfaces, a second-order polynomial model was built using a three-factor, three-level Box-Behnken design. The quantity of AFM1 was detected by the ELISA technique. The results of these experiments obtained an optimum condition in AFM1 detoxification of the three tested factors in order to maximize their effect on AFM1 detoxification in milk. The model was tested in three highly contaminated milk samples to assure the efficacy of the model. AFM1 detoxification was up to 98.4% in contaminated milk samples. These promising results provide a safe, low-cost, and low-time-consuming solution to get rid of the problem of milk contamination with AFM1.
Keywords: Box–Behnken design; L. rhamnosus; S. cerevisiae; aflatoxin M1; animal milk; antiaflatoxigenic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aflatoxin M1-Binding Ability of Selected Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains and Saccharomyces boulardii in the Experimentally Contaminated Milk Treated with Some Biophysical Factors.Arch Razi Inst. 2020 Mar;75(1):63-73. doi: 10.22092/ari.2019.123985.1265. Epub 2020 Mar 1. Arch Razi Inst. 2020. PMID: 32292004 Free PMC article.
-
Immobilization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on Perlite Beads for the Decontamination of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk.J Food Sci. 2018 Jul;83(7):2008-2013. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14100. Epub 2018 May 26. J Food Sci. 2018. PMID: 29802731
-
The transfer of aflatoxin M1 in milk of ewes fed diet naturally contaminated by aflatoxins and effect of inclusion of dried yeast culture in the diet.J Dairy Sci. 2009 Oct;92(10):4997-5004. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1684. J Dairy Sci. 2009. PMID: 19762818
-
Control of aflatoxin M1 in milk by novel methods: A review.Food Chem. 2020 May 1;311:125984. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125984. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 31855773 Review.
-
Aflatoxin M1 in Africa: Exposure Assessment, Regulations, and Prevention Strategies - A Review.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021;258:73-108. doi: 10.1007/398_2021_73. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34611756 Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted role of microbiota in liver cancer: pathogenesis, therapy, prognosis, and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 16;16:1575963. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1575963. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40589752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan-Aspirin Combination Inhibits Quorum-Sensing Synthases (lasI and rhlI) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 5;14(4):481. doi: 10.3390/life14040481. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672752 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Cariogenic and Anti-Cariogenic Potential of Human Colostrum and Colostrum-Derived Probiotics: Impact on S. mutans Growth, Biofilm Formation, and L. rhamnosus Growth.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;13(9):1869. doi: 10.3390/life13091869. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763274 Free PMC article.
-
Biodetoxification of Aflatoxin M1 in Artificially Contaminated Fermented Milk, Fermented Dairy Drink and Yogurt Using Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus reuteri, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Its Effects on Physicochemical Properties.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Apr 24;13(4):e70175. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70175. eCollection 2025 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40291925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Veldman A., Meijs J.A.C., Borggreve G.J., Heeres-van der Tol J.J. Carry-over of aflatoxin from cows’ food to milk. Anim. Prod. 1992;55:163–168. doi: 10.1017/S0003356100037417. - DOI
-
- Rahmani J., Alipour S., Miri A., Fakhri Y., Riahi S.M., Keramati H., Moradi M., Amanidaz N., Pouya R.H., Bahmani Z., et al. The prevalence of aflatoxin M1 in milk of Middle East region: A systematic review, meta-analysis and probabilistic health risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018;118:653–666. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.016. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

