Cultivable Endophyte Resources in Medicinal Plants and Effects on Hosts
- PMID: 37629552
- PMCID: PMC10455732
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081695
Cultivable Endophyte Resources in Medicinal Plants and Effects on Hosts
Abstract
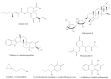
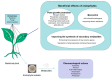
With the increasing demand for medicinal plants and the increasing shortage of resources, improving the quality and yield of medicinal plants and making more effective use of medicinal plants has become an urgent problem to be solved. During the growth of medicinal plants, various adversities can lead to nutrient loss and yield decline. Using traditional chemical pesticides to control the stress resistance of plants will cause serious pollution to the environment and even endanger human health. Therefore, it is necessary to find suitable pesticide substitutes from natural ingredients. As an important part of the microecology of medicinal plants, endophytes can promote the growth of medicinal plants, improve the stress tolerance of hosts, and promote the accumulation of active components of hosts. Endophytes have a more positive and direct impact on the host and can metabolize rich medicinal ingredients, so researchers pay attention to them. This paper reviews the research in the past five years, aiming to provide ideas for improving the quality of medicinal plants, developing more microbial resources, exploring more medicinal natural products, and providing help for the development of research on medicinal plants and endophytes.
Keywords: biocontrol; endophyte; medicinal components; medicinal plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous