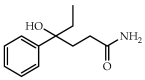
Developmental Toxicity Study of DL-4-Hydroxy-4-Phenylhexanamide (DL-HEPB) in Rats
- PMID: 37629571
- PMCID: PMC10455234
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081714
Developmental Toxicity Study of DL-4-Hydroxy-4-Phenylhexanamide (DL-HEPB) in Rats
Abstract
Antiepileptic drugs affect embryonic development when administered during pregnancy, generating severe alterations, such as as cleft lip, spina bifida, heart abnormalities, or neuronal alterations. The compound DL-4-hydroxy-4-phenylhexanamide (DL-HEPB), a phenyl alcohol amide structurally different from known anticonvulsants, has shown good anticonvulsant effects in previous studies. However, its effects on intrauterine development are unknown. So, the purpose of this study was to determine the potential of DL-HEPB to produce alterations in conceptus. Pregnant Wistar rats were orally exposed to 0, 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg of DL-HEPB during organogenesis, and their food consumption and weight gain were measured. On gestation day 21, pregnant females were euthanized to analyze the fetuses for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations. A significant decrease in food consumption and body weight was observed in mothers, without any other manifestation of toxicity. In fetuses, no external malformations, visceral, or skeletal abnormalities, were observed under the dose of 100 mg/kg, while the dose of 200 mg/kg caused malformations in low frequency in brain and kidneys. In view of the results obtained, DL-HEPB could be a good starting point for the design of new highly effective anticonvulsant agents, with much lower developmental toxicity than that shown by commercial anticonvulsants.
Keywords: DL-4-hydroxy-4-phenylhexanamide; anticonvulsant; developmental; rats; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of R-[3H]-baclofen binding to rat brain synaptic membranes by a homologous series of phenyl alcohol amides anticonvulsants and their evaluation as GABAB receptor blockers.Arzneimittelforschung. 1998 Nov;48(11):1051-7. Arzneimittelforschung. 1998. PMID: 9850423
-
Evaluation of the toxic and teratogenic potential of the anticonvulsant drug 4-hydroxy, 4-ethyl, 4-phenylbutyramide in mice.Arch Med Res. 1994 Winter;25(4):441-6. Arch Med Res. 1994. PMID: 7858404
-
Embryo-fetal developmental toxicity of carbamazepine administered orally in wistar rat.Reprod Toxicol. 2024 Oct;129:108665. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2024.108665. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Reprod Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39009194
-
Comparison of the developmental toxicity of aspirin in rabbits when administered throughout organogenesis or during sensitive windows of development.Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2003 Feb;68(1):38-46. doi: 10.1002/bdrb.10004. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12852482
-
Developmental toxicity evaluation of 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5H)-furanone (MX) in Wistar rats.Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2003 Apr;68(2):172-9. doi: 10.1002/bdrb.10017. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12866708
References
-
- Góra M., Czopek A., Rapacz A., Dziubina A., Głuch-Lutwin M., Mordyl B., Obniska J. Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Activity of New Hybrid Compounds: Derivatives of 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:5750. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources