Structure-Based Multi-Targeted Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation of Soybean-Derived Isoflavone Genistin as a Potential Breast Cancer Signaling Proteins Inhibitor
- PMID: 37629596
- PMCID: PMC10455564
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081739
Structure-Based Multi-Targeted Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation of Soybean-Derived Isoflavone Genistin as a Potential Breast Cancer Signaling Proteins Inhibitor
Abstract
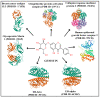
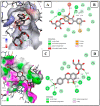
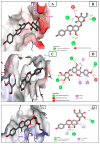
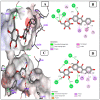
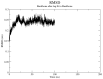
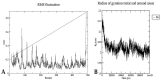
Globally, breast cancer (BC), the second-biggest cause of cancer death, occurs due to unregulated cell proliferation leading to metastasis to other parts of the human organ. Recently, the exploration of naturally derived anticancer agents has become popular due to their fewer adverse effects. Among the natural products, soybean is a very well-known legume that contains important bioactive compounds such as diadazine, glycetin, genistein, and genistin. Therefore, keeping its therapeutic potential in mind, multi-targeted molecular docking and simulation studies were conducted to explore the potential role of soybean-derived isoflavone genistin against several breast cancer-signaling proteins (ER-alpha, ER-Beta, collapsin response mediator protein 2, CA 15-3, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2). A comparative study of the genistin-protein docked complex was explored to investigate its potential role in BC. The molecular binding energy (∆G) of the docked complex was calculated along with ADMET properties. The molecular docking score of genistin with ubiquitin-like protein activation complex-a type of Cancer Antigen (CA) 15.3 (PDB ID-2NVU, 5T6P, and 1YX8) showed the highest binding energy, ranging from -9.5 to -7.0 Kcal/mol, respectively. Furthermore, the highest docking scores of the complex were additionally put through molecular dynamics (MD) simulation analysis. MD simulations of the selected complex were performed at 100 ns to study the stability of the genistin-ubiquitin-like protein CA 15.3 complex, which appeared to be quite stable. Additionally, the ADMET study demonstrated that genistin complies with all drug-likeness standards, including Lipinski, Egan, Veber, Ghose, and Muegge. Therefore, based on the results, genistin can be considered as one of the potential drugs for the management and treatment of BC. In addition, the obtained results suggest that genistin could pave the way for new drug discovery to manage breast cancer and has potential in the development of nutraceuticals.
Keywords: breast cancer-signaling proteins; cancer; cancer antigen; genistin; isoflavone compounds; molecular dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Jha V., Devkar S., Gharat K., Kasbe S., Matharoo D.K., Pendse S., Bhosale A., Bhargava A. Screening of Phytochemicals as Potential Inhibitors of Breast Cancer using Structure Based Multitargeted Molecular Docking Analysis. Phytomed. Plus. 2022;2:100227. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100227. - DOI
-
- Abd Elmoneim O., Al-Shammari E., Alam M.J., Alcantara J.C., Khan M.A., Eltoum N.E., Ashraf S.A. Okra-Derived Dietary Carotenoid Lutein Against Breast Cancer, with an Approach towards Developing a Nutraceutical Product: A Meta-Analysis Study. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2021;33:135–142.
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

