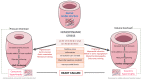
Exercise Effects on Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
- PMID: 37629599
- PMCID: PMC10456116
- DOI: 10.3390/life13081742
Exercise Effects on Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
Abstract
Left ventricular (LV) remodeling is a dynamic process, which is characterized by changes in ventricular size, shape, and wall thickness, thus altering myocardial geometry and function, and is considered as a negative prognostic factor in patients with heart failure (HF). Hypertension, type 2 diabetes (T2D), and obesity are strongly correlated with the development and the progression of LV remodeling, LV hypertrophy, and LV systolic and/or diastolic dysfunction. Indeed, the beneficial impact of exercise training on primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) has been well-established. Recent studies have highlighted that exercise training enhances functional capacity, muscle strength and endurance, cardiac function, and cardiac-related biomarkers among patients with established coronary artery disease (CAD) or HF, thus substantially improving their cardiovascular prognosis, survival rates, and need for rehospitalization. Therefore, in this review article, we discuss the evidence of LV remodeling in patients with cardiometabolic risk factors, such as hypertension, T2D, and obesity, and also highlight the current studies evaluating the effect of exercise training on LV remodeling in these patients.
Keywords: diabetes; exercise; heart failure; hypertension; obesity; ventricular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Effect of endurance training early or late after coronary artery occlusion on left ventricular remodeling, hemodynamics, and survival in rats with chronic transmural myocardial infarction.Circulation. 1994 Jan;89(1):402-12. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.1.402. Circulation. 1994. PMID: 8281676
-
Impact of aerobic interval training and continuous training on left ventricular geometry and function: a SAINTEX-CAD substudy.Int J Cardiol. 2018 Apr 15;257:193-198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.11.053. Int J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29506692 Clinical Trial.
-
Exercise-Induced Left Ventricular Remodeling Among Competitive Athletes: A Phasic Phenomenon.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Dec;8(12):e003651. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003651. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26666381
-
The effects of different initiation time of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling and cardiopulmonary rehabilitation in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(3):268-76. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1036174. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 25885667 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship of Chronic Stress and Hypertension with Bone Resorption.J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025 Jan 4;10(1):21. doi: 10.3390/jfmk10010021. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025. PMID: 39846662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Left Ventricular Shape Index and Eccentricity Index as Promising Parameters for Detection of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Cardiovascular Events.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025;21(5):42-51. doi: 10.2174/011573403X357558250122062037. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39931848 Review.
References
-
- Mortality G.B.D., Causes of Death C. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–171. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stein E.J., Fearon W.F., Elmariah S., Kim J.B., Kapadia S., Kumbhani D.J., Gillam L., Whisenant B., Quader N., Zajarias A., et al. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Biomarkers of Cardiac Damage and Stress in Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022;11:e023466. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023466. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharpe N. Left ventricular remodeling: Pathophysiology and treatment. Heart Fail. Monit. 2003;4:55–61. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous