Safety and Feasibility of Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization in Patients with Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas
- PMID: 37629648
- PMCID: PMC10456525
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59081358
Safety and Feasibility of Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization in Patients with Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas
Abstract
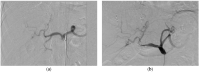
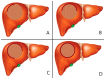
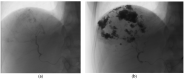
Giant hepatic hemangiomas present a significant clinical challenge, and effective treatment options are warranted. This study aimed to assess the safety and feasibility of transarterial bleomycin-lipiodol embolization in patients with giant hepatic hemangiomas. A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients with giant hepatic hemangiomas (>5 cm). Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) was performed using 7-20 cc of lipiodol mixed with 1500 IU of bleomycin. Safety outcomes, including post-embolization syndrome (PES), hepatic artery dissection, systemic complications, and access site complications, were evaluated. Radiation doses were also measured. Feasibility was assessed based on the achieved hemangioma coverage. Seventy-three patients (49 female, 24 male) with a mean age of 55.52 years were treated between December 2014 and April 2023. The average hospitalization duration was 3.82 days, and 97.3% of lesions were limited to one liver lobe. The average bleomycin dose per procedure was 1301.5625 IU, while the average lipiodol dose was 11.04 cc. The average radiation dose was 0.56 Gy. PES occurred after 45.7% of TACE procedures, with varying severity. Complications such as hepatic artery dissection (three cases), access site complications (two cases), and other complications (one case) were observed. No treatment-related mortality occurred. Hemangioma coverage exceeding 75% was achieved in 77.5% of cases. The study results suggest that transarterial bleomycin-lipiodol embolization is a safe and feasible treatment option for a heterogeneous group of patients with giant hepatic hemangiomas. This approach may hold promise in improving outcomes for patients with this challenging condition.
Keywords: bleomycin; giant hepatic hemangiomas; lipiodol; transarterial bleomycin–lipiodol embolization; transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Transarterial Chemoembolization of Giant Liver Hemangiomas with Lipiodol-Bleomycin Emulsion.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024 Nov;47(11):1506-1514. doi: 10.1007/s00270-024-03876-w. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39406873
-
Evaluation of Predictive Factors for Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization Success in Treating Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 26;17(1):42. doi: 10.3390/cancers17010042. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39796672 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization (B/LE) for Symptomatic Giant Hepatic Hemangioma.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018 Nov;41(11):1674-1682. doi: 10.1007/s00270-018-2010-4. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29922860
-
Effectiveness of Transarterial Embolization in Treatment of Symptomatic Hepatic Hemangiomas: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021 Jan;44(1):80-91. doi: 10.1007/s00270-020-02611-5. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32808203
-
Treatment of Liver Tumors with Lipiodol TACE: Technical Recommendations from Experts Opinion.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016 Mar;39(3):334-43. doi: 10.1007/s00270-015-1208-y. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26390875 Review.
Cited by
-
Transarterial embolization with bleomycin-lipiodol emulsion: a successful minimal invasive approach for giant liver hemangioma.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun;17(3):511-514. doi: 10.1007/s12328-024-01948-5. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38526803
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Transarterial Chemoembolization of Giant Liver Hemangiomas with Lipiodol-Bleomycin Emulsion.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024 Nov;47(11):1506-1514. doi: 10.1007/s00270-024-03876-w. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39406873
-
Evaluation of Predictive Factors for Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization Success in Treating Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 26;17(1):42. doi: 10.3390/cancers17010042. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39796672 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsideration of the clinical management of hepatic hemangioma.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Nov 27;16(11):3623-3628. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i11.3623. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39649192 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Chemoembolization for the Treatment of Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas: An Assessment of Effectiveness.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 16;16(2):380. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020380. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grieco M., Miscall B. Giant hemangiomas of the liver. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1978;147:783. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

