Four-Dimensional-Printed Microrobots and Their Applications: A Review
- PMID: 37630143
- PMCID: PMC10456732
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14081607
Four-Dimensional-Printed Microrobots and Their Applications: A Review
Abstract
Owing to their small size, microrobots have many potential applications. In addition, four-dimensional (4D) printing facilitates reversible shape transformation over time or upon the application of stimuli. By combining the concept of microrobots and 4D printing, it may be possible to realize more sophisticated next-generation microrobot designs that can be actuated by applying various stimuli, and also demonstrates profound implications for various applications, including drug delivery, cells delivery, soft robotics, object release and others. Herein, recent advances in 4D-printed microrobots are reviewed, including strategies for facilitating shape transformations, diverse types of external stimuli, and medical and nonmedical applications of microrobots. Finally, to conclude the paper, the challenges and the prospects of 4D-printed microrobots are highlighted.
Keywords: 4D-printed; applications; medical; microrobots; nonmedical; shape reversible; stimuli-responsive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
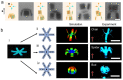


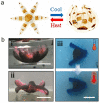
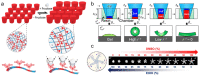
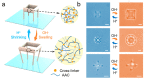

References
-
- Zhang L., Abbott J.J., Dong L., Kratochvil B.E., Bell D., Nelson B.J. Artificial Bacterial Flagella: Fabrication and Magnetic Control. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009;94:064107. doi: 10.1063/1.3079655. - DOI
-
- Vrba J., Maslen C., Maxova J., Duras J., Rehor I., Mares J. An Automated Platform for Assembling Light-Powered Hydrogel Microrobots and Their Subsequent Chemical Binding [Formula Presented] J. Comput. Sci. 2021;55:101446. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2021.101446. - DOI
-
- Luo M., Feng Y., Wang T., Guan J. Micro-/Nanorobots at Work in Active Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018;28:1706100. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201706100. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

