Digital Microfluidic Multiplex RT-qPCR for SARS-CoV-2 Detection and Variants Discrimination
- PMID: 37630161
- PMCID: PMC10456927
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14081627
Digital Microfluidic Multiplex RT-qPCR for SARS-CoV-2 Detection and Variants Discrimination
Abstract
Continuous mutations have occurred in the genome of the SARS-CoV-2 virus since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. The increased transmissibility of the mutated viruses has not only imposed medical burdens but also prolonged the duration of the pandemic. A point-of-care (POC) platform that provides multitarget detection will help to track and reduce disease transmissions. Here we detected and discriminated three genotypes of SARS-CoV-2, including the wildtype and two variants of concern (VOCs), the Delta variant and Omicron variant, through reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) on a digital microfluidics (DMF)-based cartridge. Upon evaluating with the RNA samples of Omicron variant, the DMF RT-qPCR presented a sensitivity of 10 copies/μL and an amplification efficiency of 96.1%, capable for clinical diagnosis. When spiking with SARS-CoV-2 RNA (wildtype, Delta variant, or Omicron variant) and 18S rDNA, the clinical analog samples demonstrated accurate detection and discrimination of different SARS-CoV-2 strains in 49 min.
Keywords: COVID-19; Delta variant; Omicron variant; RT-qPCR; SARS-CoV-2; digital microfluidics; electrowetting.
Conflict of interest statement
S.K.F. is a member of the scientific advisory board for GEMFluidix. His spouse holds ownership in GEMFluidix.
Figures
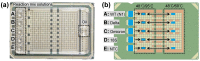

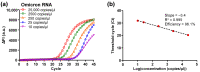
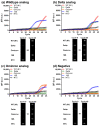
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 30 June 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Total COVID-19 Vaccine Doses Administered. [(accessed on 30 June 2023)]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/cumulative-covid-vaccinations.
-
- What COVID-19 Variants Are Going Around in June 2023? [(accessed on 30 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.nebraskamed.com/COVID/what-covid-19-variants-are-going-around.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

