Methods of Analysis and Identification of Betulin and Its Derivatives
- PMID: 37630198
- PMCID: PMC10458966
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28165946
Methods of Analysis and Identification of Betulin and Its Derivatives
Abstract
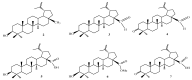
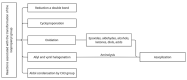
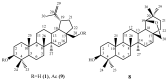
This scientific work presents practical and theoretical material on the methods of analysis and identification of betulin and its key derivatives. The properties of betulin and its derivatives, which are determined by the structural features of this class of compounds and their tendency to form dimers, polymorphism and isomerization, are considered. This article outlines ways to improve not only the bioavailability but also the solubility of triterpenoids, as well as any hydrophobic drug substances, through chemical transformations by introducing various functional groups, such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, amino, phosphate/phosphonate and carbonyl. The authors of this article summarized the physicochemical characteristics of betulin and its compounds, systematized the literature data on IR and NMR spectroscopy and gave the melting temperatures of key acids and aldehydes based on betulin.
Keywords: betulin; bioavailability; chemical transformation; the solubility of pentacyclic triterpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Şoica C.M., Dehelean C.A., Peev C., Aluas M., Zupko I., Kasa P., Alexa E. Physico-chemical comparison study of betulinic acid, betulin and birch bark extract and in vitro investigation of their cytotoxic effects towards skin epidermoid carcinoma (A431), breast carcinoma (MCF7) and cervix adenocarcinoma (HeLa) cell-lines. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012;26:968–974. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2010.545352. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

