Accelerator-Based Production of Scandium Radioisotopes for Applications in Prostate Cancer: Toward Building a Pipeline for Rapid Development of Novel Theranostics
- PMID: 37630292
- PMCID: PMC10458970
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28166041
Accelerator-Based Production of Scandium Radioisotopes for Applications in Prostate Cancer: Toward Building a Pipeline for Rapid Development of Novel Theranostics
Abstract
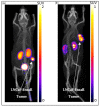
In the field of nuclear medicine, the β+ -emitting 43Sc and β- -emitting 47Sc are promising candidates in cancer diagnosis and targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT) due to their favorable decay schema and shared pharmacokinetics as a true theranostic pair. Additionally, scandium is a group-3 transition metal (like 177Lu) and exhibits affinity for DOTA-based chelators, which have been studied in depth, making the barrier to implementation lower for 43/47Sc than for other proposed true theranostics. Before 43/47Sc can see widespread pre-clinical evaluation, however, an accessible production methodology must be established and each isotope's radiolabeling and animal imaging capabilities studied with a widely utilized tracer. As such, a simple means of converting an 18 MeV biomedical cyclotron to support solid targets and produce 43Sc via the 42Ca(d,n)43Sc reaction has been devised, exhibiting reasonable yields. The NatTi(γ,p)47Sc reaction is also investigated along with the successful implementation of chemical separation and purification methods for 43/47Sc. The conjugation of 43/47Sc with PSMA-617 at specific activities of up to 8.94 MBq/nmol and the subsequent imaging of LNCaP-ENZaR tumor xenografts in mouse models with both 43/47Sc-PSMA-617 are also presented.
Keywords: PET; PSMA-617; SPECT; Scandium-43; Scandium-47; TRT; mCRPC; prostate cancer; radioisotopes; theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. Certain commercial equipment, instruments, or materials are identified in this paper to foster understanding. Such identification does not imply recommendation by the authors or their affiliated institutions, nor does it imply that the materials or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Figures










References
-
- Gomes Marin J.F., Nunes R.F., Coutinho A.M., Zaniboni E.C., Costa L.B., Barbosa F.G., Queiroz M.A., Cerri G.G., Buchpiguel C.A. Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine: Emerging and Re-Emerging Integrated Imaging and Therapies in the Era of Precision Oncology. Radiographics. 2020;40:1715–1740. doi: 10.1148/rg.2020200021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mandiwana V., Kalombo L., Hayeshi R., Zeevaart J.R., Ebenhan T. Preclinical Assessment Addressing Intravenous Administration of a [(68)Ga]Ga-PSMA-617 Microemulsion: Acute In Vivo Toxicity, Tolerability, PET Imaging, and Biodistribution. Molecules. 2021;26:2650. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

