Isolation and Anticancer Progression Evaluation of the Chemical Constituents from Bridelia balansae Tutcher
- PMID: 37630417
- PMCID: PMC10457964
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28166165
Isolation and Anticancer Progression Evaluation of the Chemical Constituents from Bridelia balansae Tutcher
Abstract
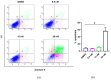
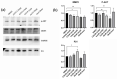
The dichloromethane extract of the roots of Bridelia balansae Tutcher (Phyllanthaceae) was found to show potential anticancer activity against HCT116 colorectal cancer cell. Our bioassay-guided phytochemical investigation of the roots of B. balansae led to the identification of 14 compounds including seven lignans (1-7), three phenylbenzene derivatives (8-10), two flavanone (11-12), and two triterpenoids (13-14). Among them, 4'-demethyl-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin (1) is the first aryltetralin lignan compound identified from this plant species. In addition, the stereochemistry of 1 was validated by X-ray crystallography for the first time, and its distinguished cytotoxic effect on HCT116 cells with an IC50 value at 20 nM was induced via an apoptosis induction mechanism. Compound 1 could also significantly decrease the migration rate of HCT116 cells, indicating its potential application against cancer metastasis. The western blot analysis showed that 1 has the potential to inhibit cell proliferation and metastasis. Treatment of 1 resulted in the downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases 2 (MMP2) and p-Akt, while p21 was upregulated. Collectively, the present study on the phytochemical and biological profile of B. balansae has determined the plant as a useful source to produce promising anticancer lead compounds.
Keywords: Bridelia balansae; apoptosis; colorectal cancer; cytotoxicity; lignan compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sumatranins A-J: Lignans with Immunosuppressive Activity from Cleistanthus sumatranus.J Nat Prod. 2023 Jun 23;86(6):1606-1614. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00300. Epub 2023 Jun 12. J Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 37307145
-
A study of the potential anticancer activity of Mangifera zeylanica bark: Evaluation of cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of the hexane extract and bioassay-guided fractionation to identify phytochemical constituents.Oncol Lett. 2016 Feb;11(2):1335-1344. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4087. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26893740 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Lignans from Zanthoxylum alatum Roxb. stem bark with cytotoxic potential.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 27;152(1):106-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.039. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24412550
-
A comprehensive insight into the antineoplastic activities and molecular mechanisms of deoxypodophyllotoxin: Recent trends, challenges, and future outlook.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 5;928:175089. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175089. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35688183 Review.
-
New Phenolics from Linum mucronatum subsp. orientale.Bioimpacts. 2014;4(3):117-22. doi: 10.15171/bi.2014.004. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Bioimpacts. 2014. PMID: 25337464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patil S.D., Chaudhari M.A., Sapkale P.V., Chaudhari R.B. A recent review on anticancer herbal drugs. J. Drug Discov. Ther. 2013;1:77–84.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

