COVID Variants, Villain and Victory: A Bioinformatics Perspective
- PMID: 37630599
- PMCID: PMC10459809
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11082039
COVID Variants, Villain and Victory: A Bioinformatics Perspective
Abstract
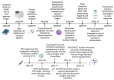
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, a novel member of the Coronaviridae family, is responsible for the viral infection known as Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). In response to the urgent and critical need for rapid detection, diagnosis, analysis, interpretation, and treatment of COVID-19, a wide variety of bioinformatics tools have been developed. Given the virulence of SARS-CoV-2, it is crucial to explore the pathophysiology of the virus. We intend to examine how bioinformatics, in conjunction with next-generation sequencing techniques, can be leveraged to improve current diagnostic tools and streamline vaccine development for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. We also emphasize how bioinformatics, in general, can contribute to critical areas of biomedicine, including clinical diagnostics, SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance and its evolution, identification of potential drug targets, and development of therapeutic strategies. Currently, state-of-the-art bioinformatics tools have helped overcome technical obstacles with respect to genomic surveillance and have assisted in rapid detection, diagnosis, and delivering precise treatment to individuals on time.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; bioinformatics; drug design; genomics; immunoinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analyses of bioinformatics applications in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Dec;95:107599. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2021.107599. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34773807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emergency SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern: Novel Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Rapid Detection and Surveillance.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0251321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02513-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196812 Free PMC article.
-
Essential interpretations of bioinformatics in COVID-19 pandemic.Meta Gene. 2021 Feb;27:100844. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2020.100844. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Meta Gene. 2021. PMID: 33349792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):524-540. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2031274. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35132910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control Control and Prevention SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. [(accessed on 25 March 2023)];2023 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classificatio....
-
- WHO Updated Working Definitions and Primary Actions for SARS-CoV-2 Variants. 2023. [(accessed on 14 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/updated-working-definitions-and-....
-
- World Health Organization Statement on the Update of WHO’s Working Definitions and Tracking System for SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Variants of Interest. 2023. [(accessed on 14 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/16-03-2023-statement-on-the-update-of-who-.... - PMC - PubMed
-
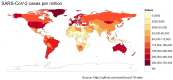
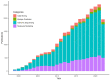
- Mathieu E., Ritchie H., Rodés-Guirao L., Appel C., Gavrilov D., Giattino C., Hasell J., Macdonald B., Dattani S., Beltekian D., et al. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19) 2020. [(accessed on 16 June 2023)]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-cases/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous