Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Caries, and Periodontitis: Syndemic Framework
- PMID: 37630703
- PMCID: PMC10458482
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15163512
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Caries, and Periodontitis: Syndemic Framework
Abstract
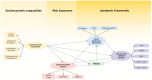
(1) Background: To investigate the grouping of obesity and insulin resistance with caries and periodontitis from a syndemic perspective through pathways of socioeconomic inequalities, smoking, alcohol, and high sugar consumption in adolescence. (2) Methods: The population-based RPS Cohort study, São Luís, Brazil, in ages 18-19 years (n = 2515) was used. The outcomes were the grouping of pbesity and Insulin Resistance Phenotype (latent variable formed by Triglycerides/HDL ratio, TyG index, and VLDL) and the Chronic Oral Disease Burden (latent variable comprising caries, bleeding on probing, probing depth ≥ 4 mm, clinical attachment level ≥ 3 mm, and visible plaque index ≥ 15%). Socioeconomic Inequalities influencing the Behavioral Risk Factors (latent variable formed by added sugar, smoking, and alcohol) were analyzed using structural equation modeling. (3) Results: Socioeconomic Inequalities were associated with the Chronic Oral Disease Burden [Standardized Coefficient (SC) = 0.222, p < 0.001]. Behavioral Risk Factors were associated with increased Chronic Oral Disease Burden (SC = 0.103; p = 0.013). Obesity was associated with the Insulin Resistance Phenotype (SC = 0.072; p < 0.001) and the Chronic Oral Disease Burden (SC = 0.066; p = 0.005). The Insulin Resistance Phenotype and the Chronic Oral Disease Burden were associated (SC = 0.053; p = 0.032). (4) Conclusion: The grouping of obesity and early events of diabetes with caries and periodontitis call for a syndemic approach in adolescence.
Keywords: adolescents; caries; insulin resistance; obesity; periodontitis; syndemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Network, Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019); Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) 2020. [(accessed on 1 June 2023)]. Available online: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool.
-
- Carmo C.D.S.S., Ribeiro M.R.C.C., Teixeira J.X.P.P., Alves C.M.C.C., Franco M.M., França A.K.T.C.T.C., Benatti B.B., Cunha-Cruz J., Ribeiro C.C.C.C., Cunha-Cruz J., et al. Added Sugar Consumption and Chronic Oral Disease Burden among Adolescents in Brazil. J. Dent. Res. 2018;97:508–514. doi: 10.1177/0022034517745326. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous