Protection of Inonotus hispidus (Bull.) P. Karst. against Chronic Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Its Relieving Inflammation Response
- PMID: 37630721
- PMCID: PMC10458315
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15163530
Protection of Inonotus hispidus (Bull.) P. Karst. against Chronic Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Its Relieving Inflammation Response
Abstract
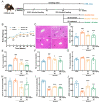
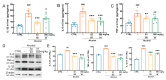
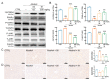
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) can be induced by excessive alcohol consumption, and has a worldwide age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of approximately 5.243%. Inonotus hispidus (Bull.) P. Karst. (IH) is a mushroom with pharmacological effects. In ALD mice, the hepatoprotective effects of IH were investigated. IH strongly ameliorated alcohol-induced pathological changes in the liver, including liver structures and its function-related indices. Intestinal microbiota and serum metabolomics analysis showed that IH altered the associated anti-inflammatory microbiota and metabolites. According to results obtained from Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), IH downregulated the levels of pro-inflammation factors interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), enhanced the expressions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and 15-hydroxprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH), and inhibited the phosphorylated activation of Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3, confirming the hepatoprotection of IH against alcohol damage via anti-inflammation. This study provides the experimental evidence for the hepatoprotective effects of IH in chronic ALD.
Keywords: Inonotus hispidus; chronic alcohol damage; hepatoprotection; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inonotus hispidus Protects against Hyperlipidemia by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation through Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling in High Fat Diet Fed Mice.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 24;14(17):3477. doi: 10.3390/nu14173477. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36079733 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Colorectal Cancer Effects of Inonotus hispidus (Bull.: Fr.) P. Karst. Spore Powder through Regulation of Gut Microbiota-Mediated JAK/STAT Signaling.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 12;14(16):3299. doi: 10.3390/nu14163299. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014805 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG combined with inosine ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury through regulation of intestinal barrier and Treg/Th1 cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 15;439:115923. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.115923. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35176292
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:495156. doi: 10.1155/2013/495156. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 24385684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li H.L., Xie Z.Y., Zhang Y., Liu Y., Niu A.J., Liu Y.Y., Zhang L.B., Guan L.L. Rosa rugosa polysaccharide attenuates alcoholic liver disease in mice through the gut-liver axis. Food Biosci. 2021;44:101385. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101385. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

