Is There More to Olive Oil than Healthy Lipids?
- PMID: 37630815
- PMCID: PMC10459315
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15163625
Is There More to Olive Oil than Healthy Lipids?
Abstract
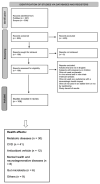
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy dietary pattern whose main characteristic is olive oil consumption. The potential health benefits of olive oil have been extensively investigated and the present review provides the more recent clinical evidence supporting the positive impact of olive oil intake on human health. PubMed (n = 227) and Scopus (n = 308) databases were searched for published clinical studies in English over the past six years (October 2016 to December 2022), following key word searches of "olive oil" and "health". Major findings associated olive oil with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, improvement in endothelial function and lipid profile, prevention of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and modulation of the gut microbiota. These benefits are attributed to the nutritional composition of olive oil, which has a high content of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) (oleic acid in particular) and minor compounds such as polyphenols (oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol). Although additional research continues to be required, the more recently generated evidence supports the potential of olive oil to contribute beneficially to health and to the prevention and management of a variety of non-communicable diseases, as a consequence of the synergism between its components' complexity.
Keywords: human health benefits; olive oil; review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- International Olive Council Designations and Definitions of Olive Oils. [(accessed on 16 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/olive-world/olive-oil/
-
- International Olive Council EU Olive Oil Figures: Consumption. [(accessed on 16 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/HO-CE90....
-
- International Olive Council EU Olive Oil Figures: Production. [(accessed on 16 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/HO-CE90....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous