Modified Mediterranean-Ketogenic Diet and Carboxytherapy as Personalized Therapeutic Strategies in Lipedema: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 37630844
- PMCID: PMC10457774
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15163654
Modified Mediterranean-Ketogenic Diet and Carboxytherapy as Personalized Therapeutic Strategies in Lipedema: A Pilot Study
Abstract
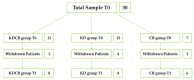
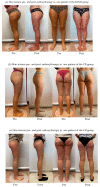
In recent years, the use of the ketogenic diet as a proper nutritional treatment for lipedema has been hypothesized in the literature. This is the first clinical study evaluating the ketogenic diet and carboxytherapy in lipedema patients. In the present study, it was decided to use a modified Mediterranean ketogenic diet (MMKD) in combination with carboxytherapy. Since lipedema is characterized by microangiopathy, local hypoxia, and increased subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) deposition, carboxytherapy could improve painful symptoms and skin tone. A total of 22 subjects were included in the data analysis, divided into three groups; 8 patients underwent MMKD combined with carboxytherapy sessions (KDCB group), 8 underwent MMKD nutritional treatment alone (KD group), and 6 patients underwent only carboxytherapy sessions (CB group), for a total of 10 weeks of treatment for all three groups. It was observed that the ketogenic diet effectively induced weight and fat mass loss, including in the limbs, areas considered unresponsive to diet therapy in lipedema patients. However, the best results were obtained from the combination of the ketogenic diet and carboxytherapy, which showed improvements in both body composition and skin texture and a reduction in pain, along with an improvement in sleep quality. It would be helpful to conduct a clinical trial on a larger scale and over a more extended period to observe the results in the long term as well.
Keywords: SAT diseases; body composition; carboxytherapy; ketogenic diet; lipedema; nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Athinarayanan S.J., Adams R.N., Hallberg S.J., McKenzie A.L., Bhanpuri N.H., Campbell W.W., Volek J.S., Phinney S.D., McCarter J.P. Long-term effects of a novel continuous remote care intervention including nutritional ketosis for the management of type 2 diabetes: A 2-year nonrandomized clinical trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2019;10:348. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McKenzie A.L., Hallberg S.J., Creighton B.C., Volk B.M., Link T.M., Abner M.K., Glon R.M., McCarter J.P., Volek J.S., Phinney S.D. A novel intervention including individualized nutritional recommendations reduces hemoglobin A1c level, medication use, and weight in type 2 diabetes. JMIR Diabetes. 2017;2:e5. doi: 10.2196/diabetes.6981. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials