Bicontinuous Cubic Liquid Crystals as Potential Matrices for Non-Invasive Topical Sampling of Low-Molecular-Weight Biomarkers
- PMID: 37631245
- PMCID: PMC10459996
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082031
Bicontinuous Cubic Liquid Crystals as Potential Matrices for Non-Invasive Topical Sampling of Low-Molecular-Weight Biomarkers
Abstract
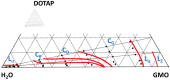
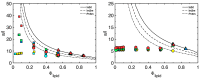
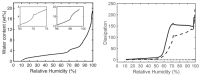
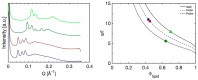
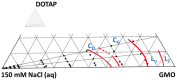
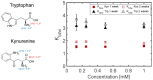
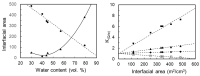
Many skin disorders, including cancer, have inflammatory components. The non-invasive detection of related biomarkers could therefore be highly valuable for both diagnosis and follow up on the effect of treatment. This study targets the extraction of tryptophan (Trp) and its metabolite kynurenine (Kyn), two compounds associated with several inflammatory skin disorders. We furthermore hypothesize that lipid-based bicontinuous cubic liquid crystals could be efficient extraction matrices. They comprise a large interfacial area separating interconnected polar and apolar domains, allowing them to accommodate solutes with various properties. We concluded, using the extensively studied GMO-water system as test-platform, that the hydrophilic Kyn and Trp favored the cubic phase over water and revealed a preference for locating at the lipid-water interface. The interfacial area per unit volume of the matrix, as well as the incorporation of ionic molecules at the lipid-water interface, can be used to optimize the extraction of solutes with specific physicochemical characteristics. We also observed that the cubic phases formed at rather extreme water activities (>0.9) and that wearing them resulted in efficient hydration and increased permeability of the skin. Evidently, bicontinuous cubic liquid crystals constitute a promising and versatile platform for non-invasive extraction of biomarkers through skin, as well as for transdermal drug delivery.
Keywords: DOTAP; X-ray diffraction; bicontinuous cubic liquid crystal; bilayer partitioning; cancer-related biomarkers; glycerol monooleate; humidity scanning (HS) QCM-D; kynurenine; non-invasive extraction; tryptophan; tryptophan-to-kynurenine ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kittler H., Pehamberger H., Wolff K., Binder M. Accuracy of the clinical diagnosis for melanoma with and without dermoscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002;119:238.
-
- Carrera C., Segura S., Aguilera P., Takigami C.M., Gomes A., Barreiro A., Scalvenzi M., Longo C., Cavicchini S., Thomas L., et al. Dermoscopy Improves the Diagnostic Accuracy of Melanomas Clinically Resembling Seborrheic Keratosis: Cross-Sectional Study of the Ability to Detect Seborrheic Keratosis-Like Melanomas by a Group of Dermatologists with Varying Degrees of Experience. Dermatology. 2017;233:471–479. doi: 10.1159/000486851. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

