Ternary Solid Dispersions: A Review of the Preparation, Characterization, Mechanism of Drug Release, and Physical Stability
- PMID: 37631330
- PMCID: PMC10459848
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082116
Ternary Solid Dispersions: A Review of the Preparation, Characterization, Mechanism of Drug Release, and Physical Stability
Abstract
The prevalence of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with low water solubility has experienced a significant increase in recent years. These APIs present challenges in formulation, particularly for oral dosage forms, despite their considerable therapeutic potential. Therefore, the improvement of solubility has become a major concern for pharmaceutical enterprises to increase the bioavailability of APIs. A promising formulation approach that can effectively improve the dissolution profile and the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs is the utilization of amorphous systems. Numerous formulation methods have been developed to enhance poorly water-soluble drugs through amorphization systems, including co-amorphous formulations, amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), and the use of mesoporous silica as a carrier. Furthermore, the successful enhancement of certain drugs with poor aqueous solubility through amorphization has led to their incorporation into various commercially available preparations, such as ASDs, where the crystalline structure of APIs is transformed into an amorphous state within a hydrophilic matrix. A novel approach, known as ternary solid dispersions (TSDs), has emerged to address the solubility and bioavailability challenges associated with amorphous drugs. Meanwhile, the introduction of a third component in the ASD and co-amorphous systems has demonstrated the potential to improve performance in terms of solubility, physical stability, and processability. This comprehensive review discusses the preparation and characterization of poorly water-soluble drugs in ternary solid dispersions and their mechanisms of drug release and physical stability.
Keywords: amorphization; amorphous solid dispersions; drug release; physical stability; poorly water-soluble drugs; ternary solid dispersion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
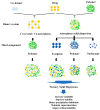
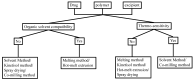
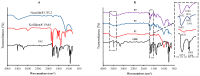
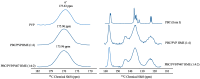
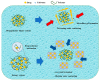
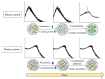
 : Preventing the water contacting to amorphous drug,
: Preventing the water contacting to amorphous drug,  : Allowing the water contacting to amorphous drug.
: Allowing the water contacting to amorphous drug.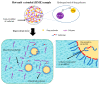

Similar articles
-
Ternary solid dispersions: classification and formulation considerations.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021 Jul;47(7):1011-1028. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2021.1908342. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33818224 Review.
-
Investigation into the Solid-State Properties and Dissolution Profile of Spray-Dried Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Rational Step toward the Design and Development of a Multicomponent Amorphous System.Mol Pharm. 2018 Sep 4;15(9):3796-3812. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00306. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30020788
-
Recent Technologies for Amorphization of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 23;13(8):1318. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081318. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs: A review.J Control Release. 2018 Dec 28;292:91-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.08.016. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30118788 Review.
-
Recent Patents on Solid Dispersions Emphasize Promising Benefits in Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-soluble Drugs.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025;19(2):216-240. doi: 10.2174/0118722105229356231030065938. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38037907 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetics of Phase Transitions in Amorphous Carbamazepine: From Sub-Tg Structural Relaxation to High-Temperature Decomposition.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;26(13):6136. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136136. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649912 Free PMC article.
-
Ternary Solid Dispersions as an Alternative Approach to Enhance Pharmacological Activity.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 3;19:5663-5684. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S533359. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40626100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanochemical Approach to Obtaining a Multicomponent Fisetin Delivery System Improving Its Solubility and Biological Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;25(7):3648. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073648. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612460 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Nintedanib Amorphous Solid Dispersions with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Aug 13;25(6):183. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02902-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39138765
References
-
- Skorupska E., Paluch P., Jeziorna A., Potrzebowski M.J. NMR Study of BA/FBA Cocrystal Con Fi Ned Within Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Employing Thermal Solid Phase Transformation. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2015;119:8652–8661. doi: 10.1021/jp5123008. - DOI
-
- DeBoyace K. Modeling and Prediction of Amorphous Solid Dispersion Formation Using a Molecular Descriptor. [(accessed on 3 March 2023)]. Available online: https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/1783/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

