Automatic Detection of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using MRI: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37631608
- PMCID: PMC10458261
- DOI: 10.3390/s23167072
Automatic Detection of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using MRI: A Systematic Review
Abstract
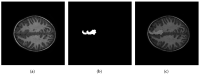
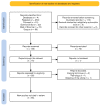
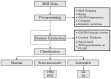
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is a congenital brain malformation that is closely associated with epilepsy. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effectively treating and managing FCD. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-one of the most commonly used non-invasive neuroimaging methods for evaluating the structure of the brain-is often implemented along with automatic methods to diagnose FCD. In this review, we define three categories for FCD identification based on MRI: visual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic methods. By conducting a systematic review following the PRISMA statement, we identified 65 relevant papers that have contributed to our understanding of automatic FCD identification techniques. The results of this review present a comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in the field of automatic FCD identification and highlight the progress made and challenges ahead in developing reliable, efficient methods for automatic FCD diagnosis using MRI images. Future developments in this area will most likely lead to the integration of these automatic identification tools into medical image-viewing software, providing neurologists and radiologists with enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Moreover, new MRI sequences and higher-field-strength scanners will offer improved resolution and anatomical detail for precise FCD characterization. This review summarizes the current state of automatic FCD identification, thereby contributing to a deeper understanding and the advancement of FCD diagnosis and management.
Keywords: deep learning; focal cortical dysplasia; image processing; machine learning; magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent advances in sMRI and artificial intelligence for presurgical planning in focal cortical dysplasia: A systematic review.J Neuroradiol. 2025 Sep;52(5):101359. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2025.101359. Epub 2025 Jun 13. J Neuroradiol. 2025. PMID: 40517890 Review.
-
Emerging translocator protein-positron emission tomographic imaging improves detection of focal cortical dysplasia.Epilepsia. 2025 Jul;66(7):2339-2352. doi: 10.1111/epi.18351. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Epilepsia. 2025. PMID: 40055993
-
Automated Detection and Localization of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II: The Optimized Detection Framework (ODF).World Neurosurg. 2025 Jun;198:124009. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2025.124009. Epub 2025 Apr 25. World Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40288525
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(18):iii-iv, ix-163. doi: 10.3310/hta12180. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462577
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Focal cortical dysplasia (type II) detection with multi-modal MRI and a deep-learning framework.Npj Imaging. 2024 Sep 2;2(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s44303-024-00031-5. Npj Imaging. 2024. PMID: 40603523 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of paediatric focal epilepsy: a narrative review.Transl Pediatr. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):1617-1633. doi: 10.21037/tp-24-166. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Transl Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39399717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

