The (Re-)Emergence and Spread of Viral Zoonotic Disease: A Perfect Storm of Human Ingenuity and Stupidity
- PMID: 37631981
- PMCID: PMC10458268
- DOI: 10.3390/v15081638
The (Re-)Emergence and Spread of Viral Zoonotic Disease: A Perfect Storm of Human Ingenuity and Stupidity
Abstract
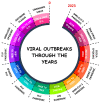
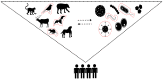
Diseases that are transmitted from vertebrate animals to humans are referred to as zoonotic diseases. Although microbial agents such as bacteria and parasites are linked to zoonotic events, viruses account for a high percentage of zoonotic diseases that have emerged. Worryingly, the 21st century has seen a drastic increase in the emergence and re-emergence of viral zoonotic disease. Even though humans and animals have coexisted for millennia, anthropogenic factors have severely increased interactions between the two populations, thereby increasing the risk of disease spill-over. While drivers such as climate shifts, land exploitation and wildlife trade can directly affect the (re-)emergence of viral zoonotic disease, globalisation, geopolitics and social perceptions can directly facilitate the spread of these (re-)emerging diseases. This opinion paper discusses the "intelligent" nature of viruses and their exploitation of the anthropogenic factors driving the (re-)emergence and spread of viral zoonotic disease in a modernised and connected world.
Keywords: (re-)emerging disease; climate change; geopolitics; globalisation; land-use change; livestock and domesticated animals; sociology; viral zoonotic disease; wildlife trade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Varela K., Brown J.A., Lipton B., Dunn J., Stanek D., Behravesh C.B., Chapman H., Conger T.H., Vanover T., Edling T., et al. A Review of Zoonotic Disease Threats to Pet Owners: A Compendium of Measures to Prevent Zoonotic Diseases Associated with Non-Traditional Pets such as Rodents and Other Small Mammals, Reptiles, Amphibians, Backyard Poultry, and Other Selected Animals. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022;22:303–360. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2022.0022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

