The efficacy of intralesional vitamin D3 injection in the treatment of cutaneous warts: A clinical therapeutic trial study
- PMID: 37632174
- PMCID: PMC10432866
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13442
The efficacy of intralesional vitamin D3 injection in the treatment of cutaneous warts: A clinical therapeutic trial study
Abstract
Background: The human papillomavirus that causes warts is usually harmless, and it can infect any part of the skin or mucous membranes. Despite the availability of several treatments, warts often return, and scarring, pigmentation changes, and recurrence are all possible side effects.
Aim: Intralesional vitamin D3 was employed as an immunotherapy for cutaneous warts in the current investigation.
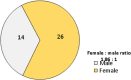
Materials and methods: In Al-Sadr Medical City in the city of Al-Najaf Al-Ashraf, a skin clinic conducted a therapeutic clinical experiment. A total of 204 cutaneous warts were examined in 40 patients (14 men and 26 females). Vitamin D3 solution of the dose (600 000 IU) was injected into the lesions' bases, with 0.2 mL per patient. Each session could only inject up to five warts. The injections were given every 2 weeks for a total of four times. Instructing patients to forego the use of any topical or oral medication was also a part of the protocol. Each patient was evaluated for recurrence risk before each therapy and then again 6 months later.
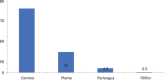
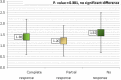
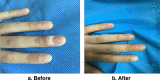
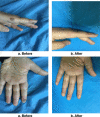
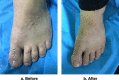
Result and discussion: There was a wide range of patient ages in this study, from 20 months to 52 years. About 65% of the cases included females. When looking at the many kinds of warts, the most prevalent was the common wart (71.6%). After four treatments, a positive response was considered to have occurred when all lesions had disappeared, a partial response when more than half of the lesions had disappeared, and no reaction when less than half of the lesions had disappeared. The final tally was 81.9% for those who responded in whole, 11.3% for those who responded partially, and 6.9% for those who did not respond at all. Next-session complete response rates were 12.7%, 29.9%, 54.9%, and 81.9%, respectively. Thirteen people experienced adverse symptoms, most noticeably minor swelling and itching. Within 6 months of follow-up, warts had completely disappeared for all patients with a partial or modest response except one who had no reaction.
Conclusion: Vitamin D3 administered intralesional is an effective and low-cost treatment for cutaneous warts.
Keywords: vitamin D; wart.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that on one of the authors has conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A comparative study of the efficacy and safety of intralesional measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine versus intralesional vitamin D3 for the treatment of warts in children.Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Sep;37(5):853-859. doi: 10.1111/pde.14280. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32681688 Clinical Trial.
-
Intralesional Vitamin D3 Injection in the Treatment of Recalcitrant Warts: A Novel Proposition.J Cutan Med Surg. 2017 Jul/Aug;21(4):320-324. doi: 10.1177/1203475417704180. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017. PMID: 28384048
-
Intralesional injection of vitamin D3 versus zinc sulfate 2% in treatment of plantar warts: a comparative study.J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 May;32(3):355-360. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1656326. Epub 2019 Aug 29. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021. PMID: 31415213
-
Emerging Intralesional Treatments for Plantar Warts: A Systematic Review.J Drugs Dermatol. 2022 Dec 1;21(12):1322-1329. doi: 10.36849/JDD.6735. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36468966
-
A review of intralesional wart therapy.Dermatol Online J. 2020 Mar 15;26(3):13030/qt3md9z8gj. Dermatol Online J. 2020. PMID: 32609439
Cited by
-
Association of vitamin D with risk of warts: A retrospective and Mendelian randomization study.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Aug;30(8):e13911. doi: 10.1111/srt.13911. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 39121007 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Vitamin D3 Derivative (Calcipotriol) Versus Intralesional Vitamin D3 in the Treatment of Cutaneous Warts: A Clinical Therapeutic Comparative Trial.Dermatol Res Pract. 2024 Nov 5;2024:5236290. doi: 10.1155/2024/5236290. eCollection 2024. Dermatol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39534647 Free PMC article.
-
Intralesional Immunotherapy for Non-Genital Viral Warts: A Review of Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 12;26(12):5644. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125644. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Randomized Comparative Study Assessing the Efficacy of Intralesional Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine and Vitamin D3 in Treating Warts.Cureus. 2025 Feb 1;17(2):e78337. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78337. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40034627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalmers R, Baker J, Griffiths C, Bleiker T, Creamer D, eds. Rook's Textbook of Dermatology. 9th ed. John Wiley; 2016.
-
- Wulf HC, Pavel S, Stender I, Bakker‐Wensveen CA. Topical photodynamic therapy for prevention of new skin lesions in renal transplant recipients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006,86(1):25‐28. - PubMed
-
- Kirnbauer R, Lenz P. Human papillomaviruses. In: Bolognia JL, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby Elsevier; 2018:1383‐1399.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

