Resting-state EEG and MEG biomarkers of pathological fatigue - A transdiagnostic systematic review
- PMID: 37632989
- PMCID: PMC10474495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103500
Resting-state EEG and MEG biomarkers of pathological fatigue - A transdiagnostic systematic review
Abstract
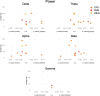
Fatigue is a highly prevalent and disabling symptom of many disorders and syndromes, resulting from different pathomechanisms. However, whether and how different mechanisms converge and result in similar symptomatology is only partially understood, and transdiagnostic biomarkers that could further the diagnosis and treatment of fatigue are lacking. We, therefore, performed a transdiagnostic systematic review (PROSPERO: CRD42022330113) of quantitative resting-state electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) studies in adult patients suffering from pathological fatigue in different disorders. Studies investigating fatigue in healthy participants were excluded. The risk of bias was assessed using a modified Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Semi-quantitative data synthesis was conducted using modified albatross plots. After searching MEDLINE, Web of Science Core Collection, and EMBASE, 26 studies were included. Cross-sectional studies revealed increased brain activity at theta frequencies and decreased activity at alpha frequencies as potential diagnostic biomarkers. However, the risk of bias was high in many studies and domains. Together, this transdiagnostic systematic review synthesizes evidence on how resting-state M/EEG might serve as a diagnostic biomarker of pathological fatigue. Beyond, this review might help to guide future M/EEG studies on the development of fatigue biomarkers.
Keywords: Biomarker; EEG; Fatigue; MEG; Systematic review; Transdiagnostic.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- (2016) In: BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and other Tools) Resource. Silver Spring (MD), Bethesda (MD).
-
- Bruno R.L., Creange S., Zimmerman J.R., Frick N.M. Elevated plasma prolactin and EEG slow wave power in post-polio fatigue. J. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. 1998;4(2):61–75.
-
- Buyukturkoglu K., Porcaro C., Cottone C., Cancelli A., Inglese M., Tecchio F. Simple index of functional connectivity at rest in Multiple Sclerosis fatigue. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017;128(5):807–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

