Mechanism-based inhibition of gut microbial tryptophanases reduces serum indoxyl sulfate
- PMID: 37633277
- PMCID: PMC10702206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.07.015
Mechanism-based inhibition of gut microbial tryptophanases reduces serum indoxyl sulfate
Abstract
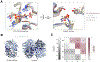
Indoxyl sulfate is a microbially derived uremic toxin that accumulates in late-stage chronic kidney disease and contributes to both renal and cardiovascular toxicity. Indoxyl sulfate is generated by the metabolism of indole, a compound created solely by gut microbial tryptophanases. Here, we characterize the landscape of tryptophanase enzymes in the human gut microbiome and find remarkable structural and functional similarities across diverse taxa. We leverage this homology through a medicinal chemistry campaign to create a potent pan-inhibitor, (3S) ALG-05, and validate its action as a transition-state analog. (3S) ALG-05 successfully reduces indole production in microbial culture and displays minimal toxicity against microbial and mammalian cells. Mice treated with (3S) ALG-05 show reduced cecal indole and serum indoxyl sulfate levels with minimal changes in other tryptophan-metabolizing pathways. These studies present a non-bactericidal pan-inhibitor of gut microbial tryptophanases with potential promise for reducing indoxyl sulfate in chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: Gut-derived uremic toxins; indoxyl sulfate; mechanism-based inhibitor; microbiome-targeted inhibition; tryptophanase.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.R.R. is a founder of Symberix Inc. M.R.R. has received research funding from Merck and Lilly, although those funds were not used in this project. A.L.G., D.P.F., and M.R.R. are inventors on US Provisional Patent Application No. 63/465,670.
Figures
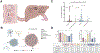
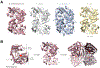
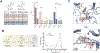
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2022). Chronic Kidney Disease Basics. https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/basics.html.
-
- Mayer et al. , 2012 (2012). The Landscape of Clinical Trials in Nephrology: A Systematic Review of ClinicalTrials.gov. Bone april, 276–285. 10.1038/jid.2014.371. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

