Polyploidy, EZH2 upregulation, and transformation in cytomegalovirus-infected human ovarian epithelial cells
- PMID: 37634008
- PMCID: PMC10555822
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-023-02813-4
Polyploidy, EZH2 upregulation, and transformation in cytomegalovirus-infected human ovarian epithelial cells
Abstract
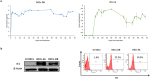
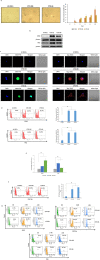
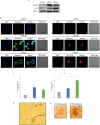
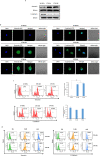
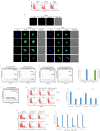
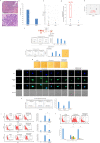
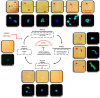
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection has been implicated in epithelial ovarian cancer (OC). Polyploidy giant cancer cells (PGCCs) have been observed in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC); they possess cancer stem cell-like characteristics and give rise to progeny cells expressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. EZH2 plays a potential oncogenic role, correlating with high proliferative index and tumor grade in OC. Herein, we present the experimental evidence for HCMV as a reprogramming vector that elicited human ovarian epithelial cells (OECs) transformation leading to the generation of "CMV-transformed Ovarian cells" (CTO). The infection with the two high-risk clinical strains, namely HCMV-DB and BL provoked a distinct cellular and molecular mechanisms in infected OECs. EZH2 upregulation and cellular proliferation were curtailed by using EZH2 inhibitors. The HGSOC biopsies were characterized by an elevated EZH2 expression, possessing a strong positive correlation between the aforementioned marker and HCMV. From HGSOC biopsies, we isolated three HCMV clinical strains that transformed OECs generating CTO cells which displayed proliferative potentials in addition to EZH2 upregulation and PGCCs generation; these features were reduced upon EZH2 inhibition. High-risk HCMV strains transformed OECs confirming an HCMV-induced epithelial ovarian cancer model and highlighting EZH2 tumorigenic properties. Our findings might be highly relevant in the pathophysiology of ovarian tumors thereby nominating new targeted therapeutics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells: A Distinctive Feature in the Transformation of Epithelial Cells by High-Risk Oncogenic HCMV Strains.Viruses. 2024 Jul 31;16(8):1225. doi: 10.3390/v16081225. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation of polyploid giant cancer cells and the transformative role of human cytomegalovirus IE1 protein.Cancer Lett. 2025 May 26:217824. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217824. Online ahead of print. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40436261
-
Polyploid giant cancer cells, EZH2 and Myc upregulation in mammary epithelial cells infected with high-risk human cytomegalovirus.EBioMedicine. 2022 Jun;80:104056. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104056. Epub 2022 May 18. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35596973 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2-Myc driven glioblastoma elicited by cytomegalovirus infection of human astrocytes.Oncogene. 2023 Jun;42(24):2031-2045. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02709-3. Epub 2023 May 5. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37147437 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2-Myc Hallmark in Oncovirus/Cytomegalovirus Infections and Cytomegalovirus' Resemblance to Oncoviruses.Cells. 2024 Mar 19;13(6):541. doi: 10.3390/cells13060541. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Transformation by Human Cytomegalovirus.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 22;16(11):1970. doi: 10.3390/cancers16111970. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893091 Free PMC article.
-
Polyploid giant cancer cells and tumor budding: translation from basic research to clinical application.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 16;15:1611920. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1611920. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40740858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of glioblastoma in mice engrafted with human cytomegalovirus-infected astrocytes.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Jul;31(7):1070-1080. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00767-7. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38553638 Free PMC article.
-
HPV and HCMV in Cervical Cancer: A Review of Their Co-Occurrence in Premalignant and Malignant Lesions.Viruses. 2024 Oct 30;16(11):1699. doi: 10.3390/v16111699. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells: A Distinctive Feature in the Transformation of Epithelial Cells by High-Risk Oncogenic HCMV Strains.Viruses. 2024 Jul 31;16(8):1225. doi: 10.3390/v16081225. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

