Interference KRT17 reverses doxorubicin resistance in triple-negative breast cancer cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- PMID: 37634232
- PMCID: PMC10504156
- DOI: 10.1007/s13258-023-01437-y
Interference KRT17 reverses doxorubicin resistance in triple-negative breast cancer cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a subtype of breast cancer with the highest degree of malignancy and is easily resistant to drugs due to the lack of hormone receptors. Research on the resistance mechanisms in TNBC is particularly important. Keratin 17 (KRT17) is highly expressed in TNBC. Anthracycline doxorubicin (Dox) is a commonly used chemotherapeutic drug for early stage triple-negative breast cancer.
Objective: This study investigated the role of KRT17 in TNBC-Dox resistance.
Methods: Immuno-histochemical staining, qPCR, western blotting (WB), and immunofluorescence were used to detect the expression of KRT17 in TNBC-Dox-resistant patients and in TNBC-Dox-resistant MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231. the effect of KRT17 on the proliferation and migration in KRT17 knockdown of TNBC-Dox-resistant cells was determined by the CCK8, clone formation, transwell invasion and wound healing assays were used to determine.
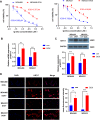
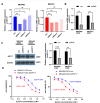
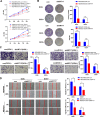
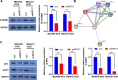
Results: KRT17 was highly expressed in the TNBC-Dox-resistant cells. Knockdown of KRT17 significantly reduced the IC50s of TNBC-Dox-resistant and parental strains and also reduced the proliferation and invasion abilities of TNBC-Dox-resistant cell lines. KRT17 regulated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The inhibitory effect of KRT17 knockdown on the proliferation and migration of TNBC-Dox-resistant cells was reversed by an activator of the Wnt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: KRT17 can inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, thereby reducing the proliferation and invasion ability of TNBC-Dox-resistant cells.
Keywords: Doxorubicin resistance; KRT17; Triple-negative breast cancer; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
