Temporal Unfolding of Racial Ingroup Bias in Neural Responses to Perceived Dynamic Pain in Others
- PMID: 37635197
- PMCID: PMC10838865
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-023-01102-0
Temporal Unfolding of Racial Ingroup Bias in Neural Responses to Perceived Dynamic Pain in Others
Abstract
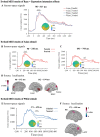
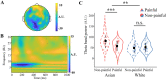
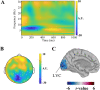
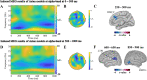
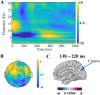
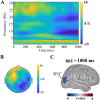
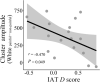
In this study, we investigated how empathic neural responses unfold over time in different empathy networks when viewing same-race and other-race individuals in dynamic painful conditions. We recorded magnetoencephalography signals from Chinese adults when viewing video clips showing a dynamic painful (or non-painful) stimulation to Asian and White models' faces to trigger painful (or neutral) expressions. We found that perceived dynamic pain in Asian models modulated neural activities in the visual cortex at 100 ms-200 ms, in the orbitofrontal and subgenual anterior cingulate cortices at 150 ms-200 ms, in the anterior cingulate cortex around 250 ms-350 ms, and in the temporoparietal junction and middle temporal gyrus around 600 ms after video onset. Perceived dynamic pain in White models modulated activities in the visual, anterior cingulate, and primary sensory cortices after 500 ms. Our findings unraveled earlier dynamic activities in multiple neural circuits in response to same-race (vs other-race) individuals in dynamic painful situations.
Keywords: Cingulate cortex; Dynamic pain; Empathy; Magnetoencephalography; Race.
© 2023. Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brown SL, Cialdini RB. Functional motives and functional consequences of prosocial behavior. In: The Oxford Handbook of Prosocial Behavior. Oxford University Press, 2015: 346–361.
-
- Johnson JD, Simmons CH, Jordav A, MacLean L, Taddei J, Thomas D, et al. Rodney King and O.J. revisited: The impact of race and defendant empathy induction on judicial decisions. J Appl Social Pyschol. 2002;32:1208–1223. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2002.tb01432.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

