Progress on Separation and Hydrothermal Carbonization of Rice Husk Toward Environmental Applications
- PMID: 37635706
- PMCID: PMC10448154
- DOI: 10.1002/gch2.202300112
Progress on Separation and Hydrothermal Carbonization of Rice Husk Toward Environmental Applications
Abstract
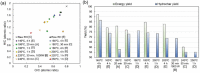
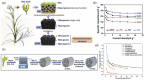
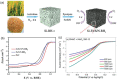
Owing to the increasing global demand for carbon resources, pressure on finite materials, including petroleum and inorganic resources, is expected to increase in the future. Efficient utilization of waste resources has become crucial for sustainable resource acquisition for creating the next generation of industries. Rice husks, which are abundant worldwide as agricultural waste, are a rich carbon source with a high silica content and have the potential to be an effective raw material for energy-related and environmental purification materials such as battery, catalyst, and adsorbent. Converting these into valuable resources often requires separation and carbonization; however, these processes incur significant energy losses, which may offset the benefits of using biomass resources in the process steps. This review summarizes and discusses the high value of RHs, which are abundant as agricultural waste. Technologies for separating and converting RHs into valuable resources by hydrothermal carbonization are summarized based on the energy efficiency of the process.
Keywords: biomass; hydrothermal carbonization; rice husk.
© 2023 The Authors. Global Challenges published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



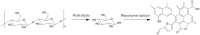

Similar articles
-
Transforming Waste into Wealth: Advanced Carbon-Based Electrodes Derived from Refinery and Coal By-Products for Next-Generation Energy Storage.Molecules. 2024 Apr 30;29(9):2081. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092081. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oil adsorbent produced by the carbonization of rice husks.Waste Manag. 2007;27(4):554-61. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.04.006. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Waste Manag. 2007. PMID: 16753291
-
Synthesis and characterization of rice husk biochar via hydrothermal carbonization for wastewater treatment and biofuel production.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 2;10(1):18851. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75936-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33139793 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Husk Research: From Environmental Pollutant to a Promising Source of Organo-Mineral Raw Materials.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jul 23;14(15):4119. doi: 10.3390/ma14154119. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34361313 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of silica and silicon from rice husk feedstock: A review.Heliyon. 2025 Feb 5;11(4):e42491. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42491. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40028602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coconut Residue-Derived Nanoporous Carbon via Hydrothermal Carbonization for Nanoporous Carbon-Based Supercapacitor Electrodes.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 25;17(13):1752. doi: 10.3390/polym17131752. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shen F., Zhu H., Luo W., Wan J., Zhou L., Dai J., Zhao B., Han X., Fu K., Hu L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23291. - PubMed
-
- Adams R. A., Dysart A. D., Esparza R., Acuña S., Joshi S. R., Cox A., Mulqueen D., Pol V. G., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8706.
-
- Gomez‐Martin A., Martinez‐Fernandez J., Ruttert M., Heckmann A., Winter M., Placke T., Ramirez‐Rico J., ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 2776. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

