Longitudinal hippocampal atrophy in hippocampal sclerosis of aging
- PMID: 37635712
- PMCID: PMC10448324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbas.2023.100092
Longitudinal hippocampal atrophy in hippocampal sclerosis of aging
Abstract
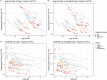
Hippocampal sclerosis of aging (HS-A) is a common degenerative neuropathology in older individuals and is associated with dementia. HS-A is characterized by disproportionate hippocampal atrophy at autopsy but cannot be diagnosed during life. Therefore, little is known about the onset and progression of hippocampal atrophy in individuals with HS-A. To better understand the onset and progression of hippocampal atrophy in HS-A, we examined longitudinal hippocampal atrophy using serial MRI in participants with HS-A at autopsy (HS-A+, n = 8) compared to participants with limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC) without HS-A (n = 13), Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic change (ADNC) without HS-A or LATE-NC (n = 16), and those without these pathologies (n = 7). We found that participants with HS-A had lower hippocampal volumes compared to the other groups, and this atrophy preceded the onset of dementia. There was also some evidence that rates of hippocampal volume loss were slightly slower in those with HS-A. Together, these results suggest that the disproportionate hippocampal atrophy seen in HS-A may begin early prior to dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease; Dementia; Hippocampal sclerosis of aging; Hippocampus; LATE-NC; MRI.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Montine T.J., Phelps C.H., Beach T.G., Bigio E.H., Cairns N.J., Dickson D.W., et al. National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2012;123:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0910-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

