Trends in tobacco smoking and smoking cessation in Russia with a focus on Indigenous populations: A narrative review
- PMID: 37635728
- PMCID: PMC10446109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gloepi.2020.100043
Trends in tobacco smoking and smoking cessation in Russia with a focus on Indigenous populations: A narrative review
Abstract
Introduction: Tobacco smoking is one of the main preventable causes of illness and premature death. Globally, more than 7 million people die annually from diseases associated with smoking, and this number is projected to increase to 8 million per year by 2030. Wide disparities in smoking prevalence exist by gender, age, socioeconomic status, rurality and ethnicity. In several countries, smoking is disproportionately high among the Indigenous populations.
Objective: This review assesses the prevalence and harm of smoking and current trends in smoking cessation among the diverse multi-ethnic populations of Russia, with a particular emphasis on Indigenous populations.
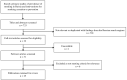
Data sources: We systematically searched health, nursing, social science and grey literature databases and bibliographies for relevant studies. Search strings combined keywords related to smoking prevalence and smoking cessation with keywords related to Russia and the Indigenous populations of Russia.
Study selection: Studies were included if they were published between 1 January 2005 and 14 October 2020, and if they reported prevalence of tobacco smoking and/or activities and outcomes of a smoking cessation programme or ban in the Russian Federation.
Conclusions: Tobacco smoking is significant in the entire Russian population, a higher prevalence of smoking in Indigenous populations compared to the dominant Russian (Slavic) ethnic group is common. Smoking prevalence data for most of the Indigenous ethnic groups of Russia remains unclear. Tobacco control interventions for Indigenous groups are underdeveloped even though they have the potential to deliver proportionately greater reduction in smoking harm.
Keywords: Cessation; Prevalenceharmindigenous; Russia; Smoking; Tobacco; Tobacco control.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017. WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2017: Monitoring tobacco use and prevention policies.
-
- Forouzanfar M.H., Afshin A., Alexander L.T., Anderson H.R., Bhutta Z.A., Biryukov S., et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1659–1724. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2011. WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2011: Warning about the dangers of tobacco.
-
- David P. Basic economic gap related to smoking: reconciling tobacco tax receipts and economic costs of smoking-attributable diseases. Tob. Control. 2019;28:558–561. - PubMed
-
- Dmitriyeva E., Tuigg D., Dyomin A., et al. Stop consumption of tobacco and treament of tobacco dependance. Scientifically-based Recommendations Narkologiya. 2013;12:44–60.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources