Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives of Exosomes as Nanocarriers in Diagnosis and Treatment of Diseases
- PMID: 37635911
- PMCID: PMC10454833
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S417422
Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives of Exosomes as Nanocarriers in Diagnosis and Treatment of Diseases
Abstract
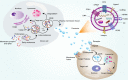
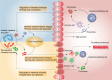
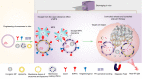
Exosomes, as natural nanocarriers, characterized with low immunogenicity, non-cytotoxicity and targeted delivery capability, which have advantages over synthetic nanocarriers. Recently, exosomes have shown great potential as diagnostic markers for diseases and are also considered as a promising cell-free therapy. Engineered exosomes have significantly enhanced the efficacy and precision of delivering therapeutic agents, and are currently being extensively employed in targeted therapeutic investigations for various ailments, including oncology, inflammatory disorders, and degenerative conditions. Particularly, engineered exosomes enable therapeutic agent loading, targeted modification, evasion of MPS phagocytosis, intelligent control, and bioimaging, and have been developed as multifunctional nano-delivery platforms in recent years. The utilization of bioactive scaffolds that are loaded with exosome delivery has been shown to substantially augment retention, extend exosome release, and enhance efficacy. This approach has advanced from conventional hydrogels to nanocomposite hydrogels, nanofiber hydrogels, and 3D printing, resulting in superior physical and biological properties that effectively address the limitations of natural scaffolds. Additionally, plant-derived exosomes, which can participate in gut flora remodeling via oral administration, are considered as an ideal delivery platform for the treatment of intestinal diseases. Consequently, there is great interest in exosomes and exosomes as nanocarriers for therapeutic and diagnostic applications. This comprehensive review provides an overview of the biogenesis, composition, and isolation methods of exosomes. Additionally, it examines the pathological and diagnostic mechanisms of exosomes in various diseases, including tumors, degenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Furthermore, this review highlights the significance of gut microbial-derived exosomes. Strategies and specific applications of engineered exosomes and bioactive scaffold-loaded exosome delivery are further summarized, especially some new techniques such as large-scale loading technique, macromolecular loading technique, development of multifunctional nano-delivery platforms and nano-scaffold-loaded exosome delivery. The potential benefits of using plant-derived exosomes for the treatment of gut-related diseases are also discussed. Additionally, the challenges, opportunities, and prospects of exosome-based nanocarriers for disease diagnosis and treatment are summarized from both preclinical and clinical viewpoints.
Keywords: diagnosis; diseases; exosomes; nanocarriers; treatment.
© 2023 Zou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 23;18:7923-7940. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S444582. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38152837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-free synthesis of connexin 43-integrated exosome-mimetic nanoparticles for siRNA delivery.Acta Biomater. 2019 Sep 15;96:517-536. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31284098
-
State-of-the-art exosome loading and functionalization techniques for enhanced therapeutics: a review.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020 Sep;40(6):804-820. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1785385. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32605394 Review.
-
Exosome-based platforms for treatment of multiple sclerosis.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Mar;222:111256. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111256. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39952444 Review.
-
Optimization of exosome-based cell-free strategies to enhance endogenous cell functions in tissue regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2023 Nov;171:68-84. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.09.023. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37730080 Review.
Cited by
-
Different origin-derived exosomes and their clinical advantages in cancer therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 27;15:1401852. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1401852. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38994350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and Near-Future Technologies to Quantify Nanoparticle Therapeutic Loading Efficiency and Surface Coating Efficiency with Targeted Moieties.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;12(4):362. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12040362. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: A Review of Their Therapeutic Potentials, Sources, Biodistribution, and Administration Routes.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 13;20:3175-3199. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S502591. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40098717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes-Based Nanotherapeutic Strategies: An Important Approach for Spinal Cord Injury Repair.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Aug 27;20:10407-10431. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S539673. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40896803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An exosome-based nanoplatform for siRNA delivery combined with starvation therapy promotes tumor cell death through autophagy, overcoming refractory KRAS-mutated tumors and restoring cetuximab chemosensitivity.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Apr 10;32:101732. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101732. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40290881 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

