Regulation of autophagy by natural polyphenols in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: therapeutic potential and mechanism
- PMID: 37635982
- PMCID: PMC10448531
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1142276
Regulation of autophagy by natural polyphenols in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: therapeutic potential and mechanism
Abstract
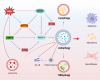
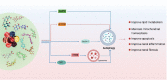
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a major microvascular complication of diabetes and a leading cause of end-stage renal disease worldwide. Autophagy plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis in renal physiology. In DKD, the accumulation of advanced glycation end products induces decreased renal autophagy-related protein expression and transcription factor EB (TFEB) nuclear transfer, leading to impaired autophagy and lysosomal function and blockage of autophagic flux. This accelerates renal resident cell injury and apoptosis, mediates macrophage infiltration and phenotypic changes, ultimately leading to aggravated proteinuria and fibrosis in DKD. Natural polyphenols show promise in treating DKD by regulating autophagy and promoting nuclear transfer of TFEB and lysosomal repair. This review summarizes the characteristics of autophagy in DKD, and the potential application and mechanisms of some known natural polyphenols as autophagy regulators in DKD, with the goal of contributing to a deeper understanding of natural polyphenol mechanisms in the treatment of DKD and promoting the development of their applications. Finally, we point out the limitations of polyphenols in current DKD research and provide an outlook for their future research.
Keywords: autophagy; diabetic kidney disease; lysosome; natural polyphenols; transcription factor EB.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Jin, Yang, Mao, Ma, Wang, Li and Zhan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

