Proximal humerus fractures: A review of current practice
- PMID: 37636006
- PMCID: PMC10457443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2023.102233
Proximal humerus fractures: A review of current practice
Abstract
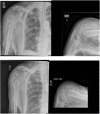
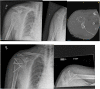
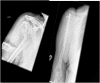
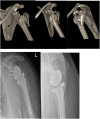
The management of proximal humeral fractures (PHF) remains controversial. Its incidence is increasing. Patients should be meticulously assessed clinically for co-morbidities and neuro-vascular injuries. Radiological investigation helps provide information on the fracture configuration and dislocations. Enhanced by 3-dimensional CT scanning, these further help in decision making and operative planning. PHF classifications have been demonstrated to have poor intra-observer and inter-observer reliability. Research has identified some radiographic predictive factors for humeral head ischaemia and likely failure of surgical fixation. The range of management options include non-operative treatment, operative fixation, intramedullary nailing and arthroplasty (hemiarthroplasty, reverse shoulder replacement). The majority of PHFs are stable injuries and non-operative management is usually successful. Some degree of malunion is readily tolerated especially by elderly patients. Surgical management of significantly displaced, unstable proximal humerus fractures should aim to stabilise the fracture adequately and provide satisfactory function for the long term. Management of the greater tuberosity is pivotal for the eventual outcome. When fixation may appear to be compromised by poor bone quality, likely poor function, age related rotator cuff degeneration or likely humeral head ischaemia clinicians may opt for arthroplasty. Successful hemiarthroplasty outcomes are dependent on sufficient healing of the tuberosity and recovery of the rotator cuff integrity. Reverse shoulder replacement can predictably deliver good functional outcomes for the shoulder in elderly patients, where rotator cuff dysfunction is suspected or as a revision procedure following failure of other surgical interventions. As opposed to hemiarthroplasty, which has shown a downward trend, there has been an increasing trend towards the use of reverse shoulder replacement in proximal humeral fractures. The management of PHFs should be patient specific, fracture specific and meet the functional demands and needs of the individual patient. The surgeon's skill set and clinical experience also plays an important role in the options of management available.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Proximal humerus fracture; Proximal humerus fracture management; Shoulder; Trauma; Upper limb.
© 2023 Delhi Orthopedic Association. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pencle F.J., Varacallo M. Treasure Island. FL; 2022. Proximal humerus fracture.
-
- Launonen A.P., Sumrein B.O., Lepola V. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Duodecim. 2017;133(4):353–358. - PubMed
-
- Clement N.D., Duckworth A.D., McQueen M.M., Court-Brown C.M. The outcome of proximal humeral fractures in the elderly: predictors of mortality and function. Bone Joint Lett J. 2014 Jul;96-B(7):970–977. - PubMed
-
- Murray I.R., Amin A.K., White T.O., Robinson C.M. Proximal humeral fractures: current concepts in classification, treatment and outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011 Jan;93(1):1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
