Functional characterization and allelic mining of OsGLR genes for potential uses in rice improvement
- PMID: 37636110
- PMCID: PMC10450912
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1236251
Functional characterization and allelic mining of OsGLR genes for potential uses in rice improvement
Abstract
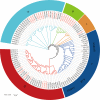
Glutamate-like receptor (GLR) genes are a group of regulatory genes involved in many physiological processes of plants. With 26 members in the rice genome, the functionalities of most rice GLR genes remain unknown. To facilitate their potential uses in rice improvement, an integrated strategy involving CRISPR-Cas9 mediated knockouts, deep mining and analyses of transcriptomic responses to different abiotic stresses/hormone treatments and gene CDS haplotype (gcHap) diversity in 3,010 rice genomes was taken to understand the functionalities of the 26 rice GLR genes, which led us to two conclusions. First, the expansion of rice GLR genes into a large gene family during evolution had gone through repeated gene duplication events occurred primarily in two large GLR gene clusters on rice chromosomes 9 and 6, which was accompanied with considerable functional differentiation. Secondly, except for two extremely conserved ones (OsGLR6.2 and OsGLR6.3), rich gcHap diversity exists at the remaining GLR genes which played important roles in rice population differentiation and rice improvement, evidenced by their very strong sub-specific and population differentiation, by their differentiated responses to day-length and different abiotic stresses, by the large phenotypic effects of five GLR gene knockout mutants on rice yield traits, by the significant association of major gcHaps at most GLR loci with yield traits, and by the strong genetic bottleneck effects and artificial selection on the gcHap diversity in populations Xian (indica) and Geng (japonica) during modern breeding. Our results suggest the potential values of the natural variation at most rice GLR loci for improving the productivity and tolerances to abiotic stresses. Additional efforts are needed to determine the phenotypic effects of major gcHaps at these GLR loci in order to identify 'favorable' alleles at specific GLR loci specific target traits in specific environments to facilitate their application to rice improvement in future.
Keywords: functional alleles; gene-CDS-haplotype (gcHap) diversity; glutamate-like receptor (GLR) genes; knockout mutants; rice improvement.
Copyright © 2023 Zeng, Li, Zhang, Wang, Rehman, Huang, Zhang, Wu, Li, Lv, Zhang, Li, Li and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of the CNGC Gene Family in Rice and Mining of Alleles for Application in Rice Improvement.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;12(24):4089. doi: 10.3390/plants12244089. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140416 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Glutamate Receptor-like Genes in Rice (Oryza sativa L.): Genome-Wide Identification, Characteristics, Evolution, Chromatin Accessibility, gcHap Diversity, Population Variation and Expression Analysis.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Dec 16;44(12):6404-6427. doi: 10.3390/cimb44120437. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36547098 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of gene-CDS-haplotype diversity in rice: Properties, population organization, footprints of domestication and breeding, and implications for genetic improvement.Mol Plant. 2021 May 3;14(5):787-804. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.02.003. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Mol Plant. 2021. PMID: 33578043
-
Candidate Genes and Pathways in Rice Co-Responding to Drought and Salt Identified by gcHap Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 5;23(7):4016. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074016. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omics: a tool for resilient rice genetic improvement strategies.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5075-5088. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07189-4. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35298758 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the CNGC Gene Family in Rice and Mining of Alleles for Application in Rice Improvement.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;12(24):4089. doi: 10.3390/plants12244089. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140416 Free PMC article.
-
Functional differentiation and genetic diversity of rice cation exchanger (CAX) genes and their potential use in rice improvement.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 15;14(1):8642. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58224-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38622172 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Rice Raffinose Synthase (OsRS) Gene Family and Haplotype Diversity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 11;25(18):9815. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189815. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337301 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of rice CXE gene family and mining of alleles for potential application in rice improvement.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 17;15:1435420. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1435420. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39483679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng Y., Tian Q., Zhang W. H. (2016). Glutamate receptors are involved in mitigating effects of amino acids on seed germination of Arabidopsis thaliana under salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 130, 68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.05.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

