Grassroots stakeholders' perception of participation in the Medium-Term Development Plan of District Assemblies in Ghana: The case of Sawla-Tuna-Kalba District
- PMID: 37636382
- PMCID: PMC10458331
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19178
Grassroots stakeholders' perception of participation in the Medium-Term Development Plan of District Assemblies in Ghana: The case of Sawla-Tuna-Kalba District
Abstract
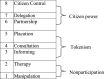
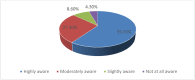
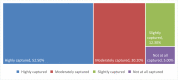
Following Ghana's decentralisation policy, the District Assemblies, in consultation with communities, are required to prepare and implement Medium-Term Development Plans [MTDPs] to ensure the overall development of their respective jurisdictions. However, little consideration has been given to the participation of grassroots stakeholders in the development of MTDPs. Consequently, this study investigates the participation of grassroots stakeholders in developing MTDPs. A cross-sectional survey involving 139 respondents was deployed. The data were gathered using a questionnaire and an interview guide, and it was analyzed using descriptive statistics, Spearman's Rank Correlation, and thematic analysis. Results indicated that grassroots stakeholders were aware of their right to participate in the preparation of MTDPs. As such, they actively participated in the process that led to developing such plans addressing community needs. Additionally, awareness of MTDP, involvement, level of influence, satisfaction with the preparation of MTDPs, satisfaction with the quality of participation in the area council, level of confidence in the preparation of MTDP, representation adequacy, and capture of community needs had statistically significant associations at the 1% level with the associations being positive. Nonetheless, the implementation of MTDPs is jeopardised by limited funding, stakeholder commitment, and human capacity. To ensure the smooth implementation of the MTDPs, the Assembly must intensify its revenue mobilisation efforts, depoliticise the MTDP process, and build staff capacity on the involvement of the grassroots stakeholders.
Keywords: Ghana; Grassroots; Local government; Medium-Term Development Plan; Participation; Stakeholder.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ei-Gack N.E. Unpublished PhD thesis, Massey University; Palmerston North, New Zealand: 2007. Participatory Approaches to Development: an Analysis of the Experiences of Development Projects in Sudan.
-
- Willis K. Routledge; London: 2005. Theories and Practices of Development.
-
- Damayanti R., Syarifuddin S. The inclusiveness of community participation in village development planning in Indonesia. Dev. Pract. 2020;30(5):624–634.
-
- Rodriguez-Pose A., Tijmastra S. 2009. On The Emergence And Significance Of Local Economic Development Strategies (CAF Working Paper, N° 2009/07)
-
- Ahmad J. vol. 3603. World Bank Publications; 2005. (Decentralisation and Service Delivery).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials