Glioblastoma survival is associated with distinct proteomic alteration signatures post chemoirradiation in a large-scale proteomic panel
- PMID: 37637066
- PMCID: PMC10448824
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1127645
Glioblastoma survival is associated with distinct proteomic alteration signatures post chemoirradiation in a large-scale proteomic panel
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Glioblastoma survival is associated with distinct proteomic alteration signatures post chemoirradiation in a large-scale proteomic panel.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 13;14:1348105. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1348105. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38544831 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Glioblastomas (GBM) are rapidly progressive, nearly uniformly fatal brain tumors. Proteomic analysis represents an opportunity for noninvasive GBM classification and biological understanding of treatment response.
Purpose: We analyzed differential proteomic expression pre vs. post completion of concurrent chemoirradiation (CRT) in patient serum samples to explore proteomic alterations and classify GBM by integrating clinical and proteomic parameters.
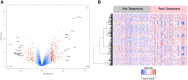
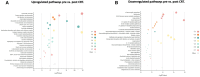
Materials and methods: 82 patients with GBM were clinically annotated and serum samples obtained pre- and post-CRT. Serum samples were then screened using the aptamer-based SOMAScan® proteomic assay. Significant traits from uni- and multivariate Cox models for overall survival (OS) were designated independent prognostic factors and principal component analysis (PCA) was carried out. Differential expression of protein signals was calculated using paired t-tests, with KOBAS used to identify associated KEGG pathways. GSEA pre-ranked analysis was employed on the overall list of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) against the MSigDB Hallmark, GO Biological Process, and Reactome databases with weighted gene correlation network analysis (WGCNA) and Enrichr used to validate pathway hits internally.
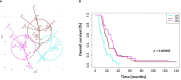
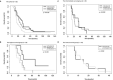
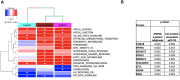
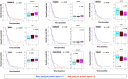
Results: 3 clinical clusters of patients with differential survival were identified. 389 significantly DEPs pre vs. post-treatment were identified, including 284 upregulated and 105 downregulated, representing several pathways relevant to cancer metabolism and progression. The lowest survival group (median OS 13.2 months) was associated with DEPs affiliated with proliferative pathways and exhibiting distinct oppositional response including with respect to radiation therapy related pathways, as compared to better-performing groups (intermediate, median OS 22.4 months; highest, median OS 28.7 months). Opposite signaling patterns across multiple analyses in several pathways (notably fatty acid metabolism, NOTCH, TNFα via NF-κB, Myc target V1 signaling, UV response, unfolded protein response, peroxisome, and interferon response) were distinct between clinical survival groups and supported by WGCNA. 23 proteins were statistically signficant for OS with 5 (NETO2, CST7, SEMA6D, CBLN4, NPS) supported by KM.
Conclusion: Distinct proteomic alterations with hallmarks of cancer, including progression, resistance, stemness, and invasion, were identified in serum samples obtained from GBM patients pre vs. post CRT and corresponded with clinical survival. The proteome can potentially be employed for glioma classification and biological interrogation of cancer pathways.
Keywords: classification; genomic; glioma; proteomic; radiation.
Copyright © 2023 Krauze, Sierk, Nguyen, Chen, Yan, Hu, Jiang, Tasci, Zgela, Sproull, Mackey, Shankavaram, Meerzaman and Camphausen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zeng J, DeVries K, Krauze A. Patterns of failure and development of a novel prognostic scoring system in elderly patients with glioblastoma – follow up on 10 year analysis of the BC cancer agency population. in Society of Neuro-Oncology 2019. Neuro-Oncology (2019). doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz175.575 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

