A sweet new set of inducible and constitutive promoters in Haloferax volcanii
- PMID: 37637112
- PMCID: PMC10448506
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1204876
A sweet new set of inducible and constitutive promoters in Haloferax volcanii
Abstract
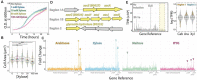
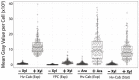
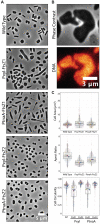
Inducible promoters are one of cellular and molecular biology's most important technical tools. The ability to deplete, replete, and overexpress genes on demand is the foundation of most functional studies. Here, we developed and characterized a new xylose-responsive promoter (Pxyl), the second inducible promoter system for the model haloarcheon Haloferax volcanii. Generating RNA-seq datasets from cultures in the presence of four historically used inducers (arabinose, xylose, maltose, and IPTG), we mapped upregulated genomic regions primarily repressed in the absence of the above inducers. We found a highly upregulated promoter that controls the expression of the xacEA (HVO_B0027-28) operon in the pHV3 chromosome. To characterize this promoter region, we cloned msfGFP (monomeric superfold green fluorescent protein) under the control of two upstream regions into a modified pTA962 vector: the first 250 bp (P250) and the whole 750 bp intergenic fragments (P750). The P250 sequence drove the expression of msfGFP constitutively, and its expression did not respond to the presence or absence of xylose. However, the P750 promoter showed not only to be repressed in the absence of xylose but also expressed higher levels of msfGFP than the previously described inducible promoter PtnaA in the presence of the inducer. Finally, we validated the inducible Pxyl promoter by reproducing morphological phenotypes already described in the literature. By overexpressing the tubulin-like FtsZ1 and FtsZ2, we observed similar but slightly more pronounced morphological defects than the tryptophan-inducible promoter PtnaA. FtsZ1 overexpression created larger, deformed cells, whereas cells overexpressing FtsZ2 were smaller but mostly retained their shape. In summary, this work contributes a new xylose-inducible promoter that could be used simultaneously with the well-established PtnaA in functional studies in H. volcanii in the future.
Keywords: Haloferax volcanii; archaea; constitutive promoters; haloarchaea; inducible promoters; xylose-inducible promoter.
Copyright © 2023 Rados, Andre, Cerletti and Bisson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
XacR - a novel transcriptional regulator of D-xylose and L-arabinose catabolism in the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii.Environ Microbiol. 2015 May;17(5):1663-76. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12603. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25141768
-
The archaeal protein SepF is essential for cell division in Haloferax volcanii.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 8;12(1):3469. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23686-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34103513 Free PMC article.
-
CdrS Is a Global Transcriptional Regulator Influencing Cell Division in Haloferax volcanii.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0141621. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01416-21. Epub 2021 Jul 13. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34253062 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake of D-xylose and L-arabinose in Haloferax volcanii involves an ABC transporter of the CUT1 subfamily.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019 Apr 1;366(8):fnz089. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnz089. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31089701
-
Development of inducer-free expression plasmids based on IPTG-inducible promoters for Bacillus subtilis.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Jul 25;16(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0747-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28743271 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Establishment of the CRISPR-Cpf1 gene editing system in Bacillus licheniformis and multiplexed gene knockout.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 8;10(1):39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.08.002. eCollection 2025. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39224148 Free PMC article.
-
Halofilins as emerging bactofilin families of archaeal cell shape plasticity orchestrators.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct;121(40):e2401583121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2401583121. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39320913 Free PMC article.
-
Haloferax volcanii: a versatile model for studying archaeal biology.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jun 24;207(6):e0006225. doi: 10.1128/jb.00062-25. Epub 2025 May 14. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40366157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salactin, a dynamically unstable actin homolog in Haloarchaea.mBio. 2023 Dec 19;14(6):e0227223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02272-23. Epub 2023 Nov 15. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37966230 Free PMC article.
-
Promoters in Pichia pastoris: A Toolbox for Fine-Tuned Gene Expression.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2844:159-178. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4063-0_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39068339 Review.
References
-
- Batt C. A., Bodis M. S., Picataggio S. K., Claps M. C., Jamas S., Sinskey A. J. (1985). Analysis of xylose operon regulation by mud (Apr, lac) fusion: trans effect of plasmid coded xylose operon. Can. J. Microbiol. 31, 930–933. doi: 10.1139/m85-174 - DOI
-
- Borghi L. (2010). “Inducible gene expression Systems for Plants” in Plant developmental biology: Methods and protocols, methods in molecular biology. eds. Hennig L., Köhler C. (Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; ), 65–75. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

