Comparative analysis of pinning techniques for supracondylar humerus fractures in paediatrics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37637498
- PMCID: PMC10457683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2023.08.005
Comparative analysis of pinning techniques for supracondylar humerus fractures in paediatrics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Purpose: Supracondylar humeral fractures (SCHFs) rank among the frequently observed fractures in children. Nonetheless, there exists a dearth of consensus regarding the optimal surgical approach. This meta-analysis aims to thoroughly evaluate and compare two distinct pinning techniques (cross pinning versus lateral pinning) for SCHFs, using data from Randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
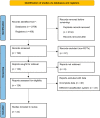
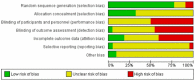
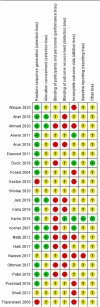
Methods: Literature review was done using PubMed, CINAHL, Scopus, and The Cochrane Library for RCTs comparing the two pinning methods and providing information on at least one of the following: Loss of Baumann's angle, loss of carrying angle, elbow function assessed based on Flynn criteria, pin tract infection, and iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury. Random effect model was used to calculate standardized mean difference or Odds Ratio (OR) for the outcomes. Review Manager 5.4.1. was used to perform quality assessment and statistical analysis.
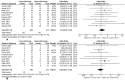
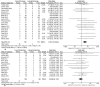
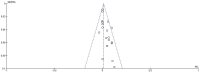
Results: A total of 22 RCTs were included. 20 studies reported data for iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury, the OR was calculated to be 3.76 (95% CI 1.75-8.06), showing a significantly lower risk of surgical ulnar nerve injury with the lateral technique. However, no significant difference was found between the pinning techniques in regard to the other outcomes.
Conclusion: In comparison to lateral pinning, the utilization of cross pinning technique exposes the patient to a heightened susceptibility of iatrogenic nerve injury. Therefore, it is recommended that surgeons prioritize the implementation of the lateral pinning technique whenever feasible, as it offers greater protection against iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury. For the other intraoperative and postoperative outcomes, both surgical techniques yield comparable results.
Keywords: Elbow; Elbow fractures; Meta-analysis; Orthopedic surgery; Randomized controlled trial; Supracondylar distal humeral fracture; Ulnar nerve.
© 2023 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lateral versus cross pinning in paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials.ANZ J Surg. 2021 May;91(5):980-985. doi: 10.1111/ans.16743. Epub 2021 Apr 1. ANZ J Surg. 2021. PMID: 33792121
-
Medial-lateral versus lateral-only pinning fixation in children with displaced supracondylar humeral fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jan 16;18(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03528-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36647086 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of lateral entry and crossed entry pinning for pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Jun 9;16(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02505-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34107972 Free PMC article.
-
Is lateral pin fixation for displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus better than crossed pins in children?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Sep;471(9):2942-53. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3025-4. Epub 2013 May 8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013. PMID: 23653099 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of lateral entry with crossed entry pinning for pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 Apr 3;13(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0768-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 29615086 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Application of elbow skin fold extension line in extreme elbow flexion in ulnar Kirschner wire insertion of extended supracondylar humeral fractures in children].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jan 15;39(1):70-74. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202409088. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39848719 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Comparative risk of ulnar nerve injury in pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a multicenter evaluation of Kirschner wire fixation techniques.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 Oct;34(7):3783-3787. doi: 10.1007/s00590-024-04101-7. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 39316133
References
-
- Gartland J.J. Management of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Surg Gynecol Obstet. Aug 1959;109(2):145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

